vdBH 15 Reflection Nebula
by Alejandro Tombolini
Introduction
Image of CEDIC team publicated by Herbert in Gallery in PixInsight Forum - Image with faint nebulosity - Main notes: Reparation of defect lines with CanonBandingReduction Script. Contrast with Adaptive Stretch on masks and special masks to work over the background with faint details and noise reduction. Date: March 2015
Processing
This image is a difficult target to process due that the faint nebulosity is mixed at the level of noise, but was taken on wonderfull skies, so I will try to push details working with masks and give contrast saturating the image.
Open RGB and L images for inspection
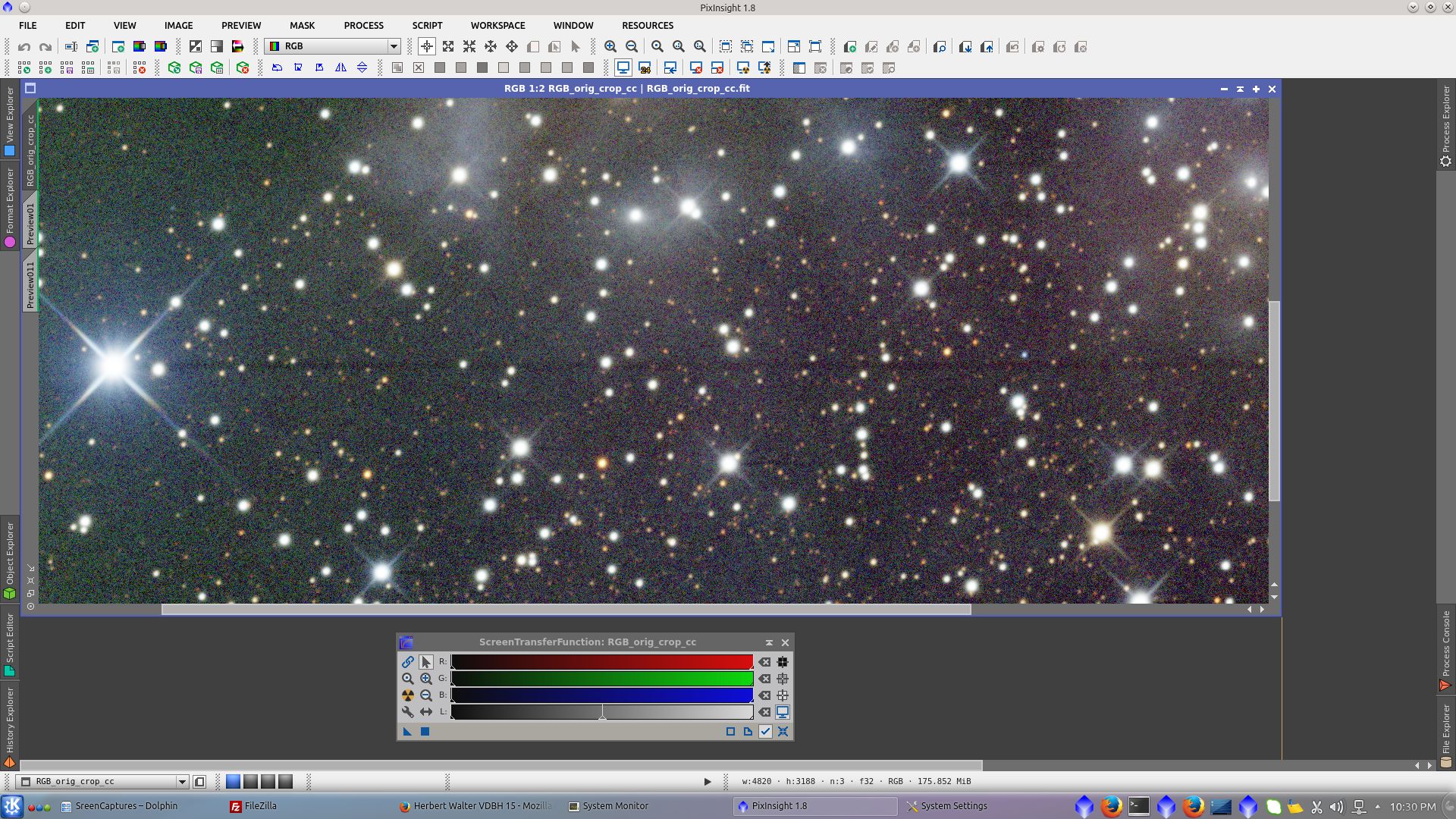
Adjust ScreenTransferFunction for better visualization of the image. Ctrl+Atomic buttom and a adjust Shadows clipping
CosmeticCorrection in L and RGB images
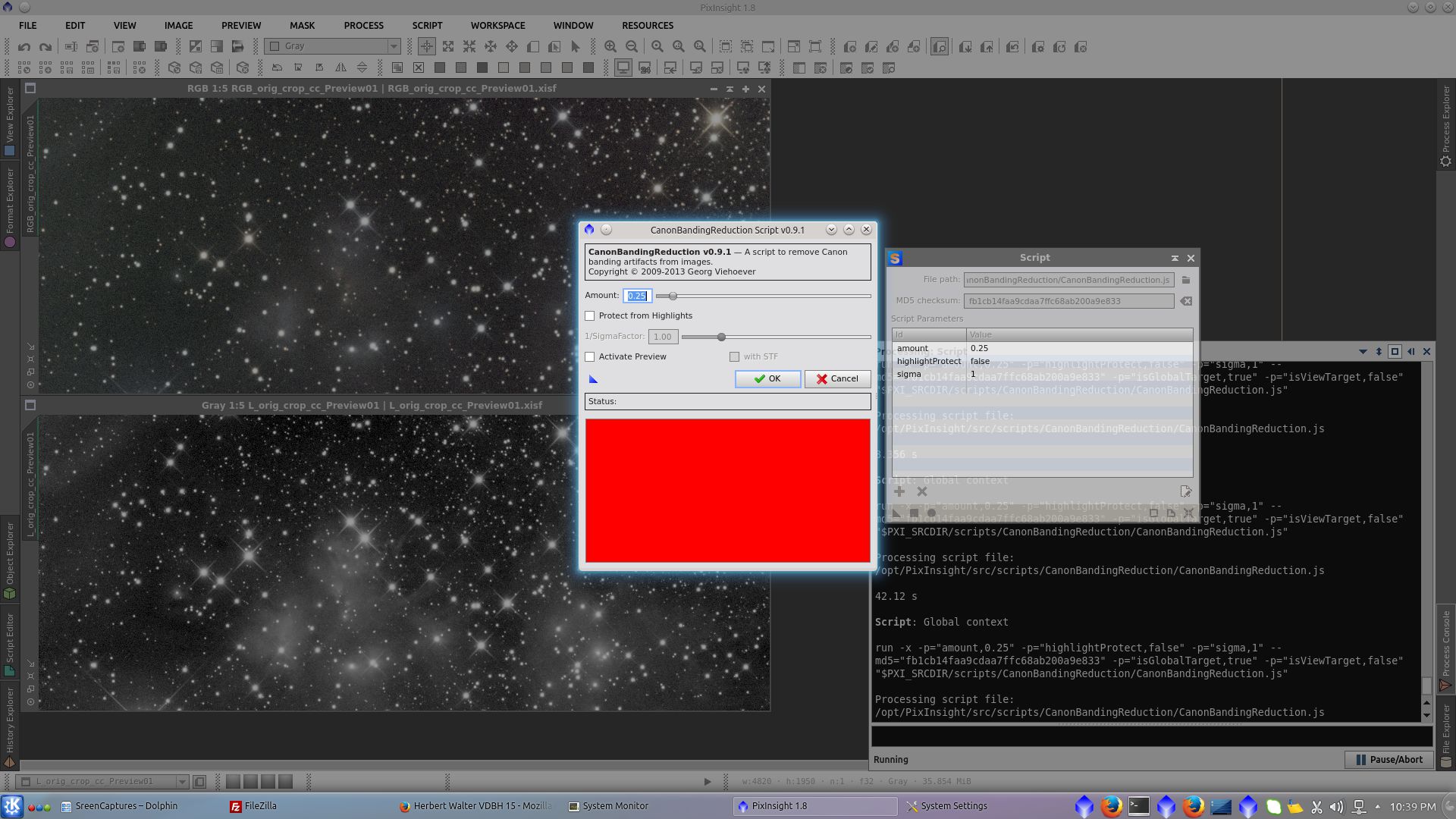
There are dark lines originated in bright stars, the brightest the star the more notorious the line. Using CanonBandingReduction I will try to minimize the big one. I did not try to correct the smallest
Found the correct settings on CBR to reduce the line, but with residual and worst effects on the rest of the image, then I decided to crop it and correct it separatly
Generate two previews, one of them including the defect and the other with certain superposition over the first in both, L and RGB images.
Perform identical CBR value to both RBG and L on upper section of the image
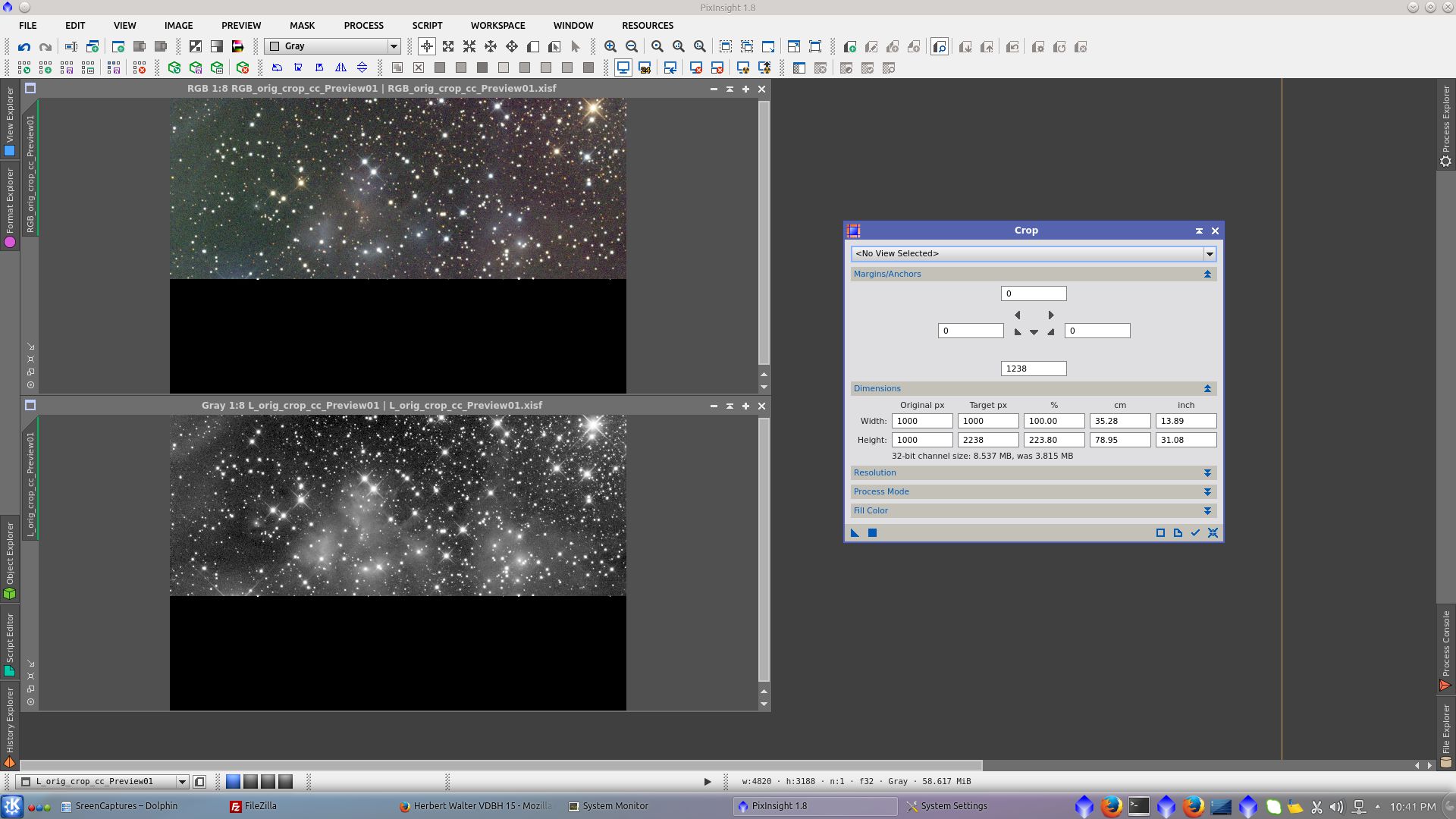
Crop both images to the original size of the image
Idem for the bottom of the image. Perform the same CBR value to both RBG and L.
Crop both images to the original size of the image
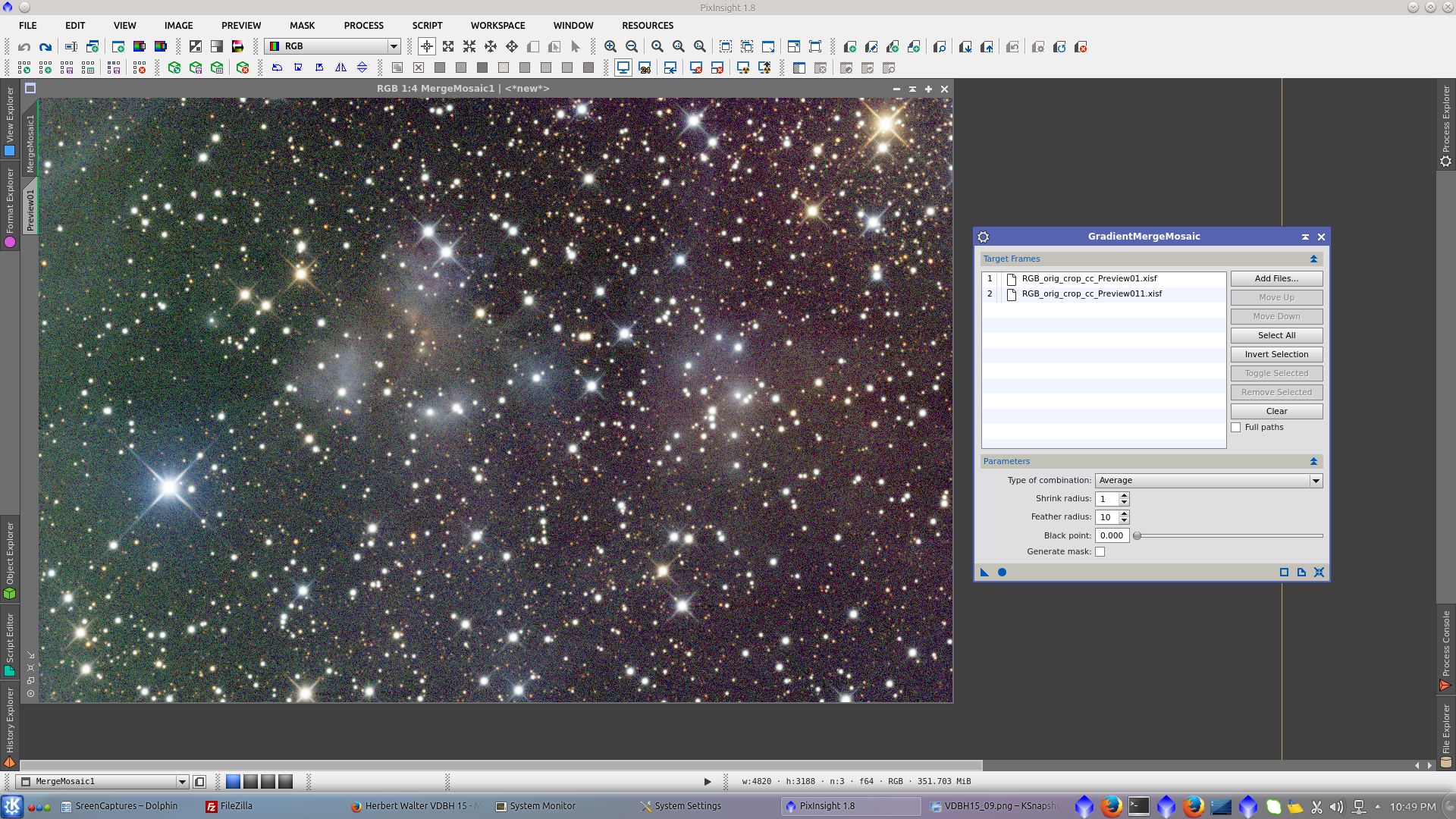
Save both RGB_previews and use GradientMergeMosaic to reconstruct RGB image without the dark line
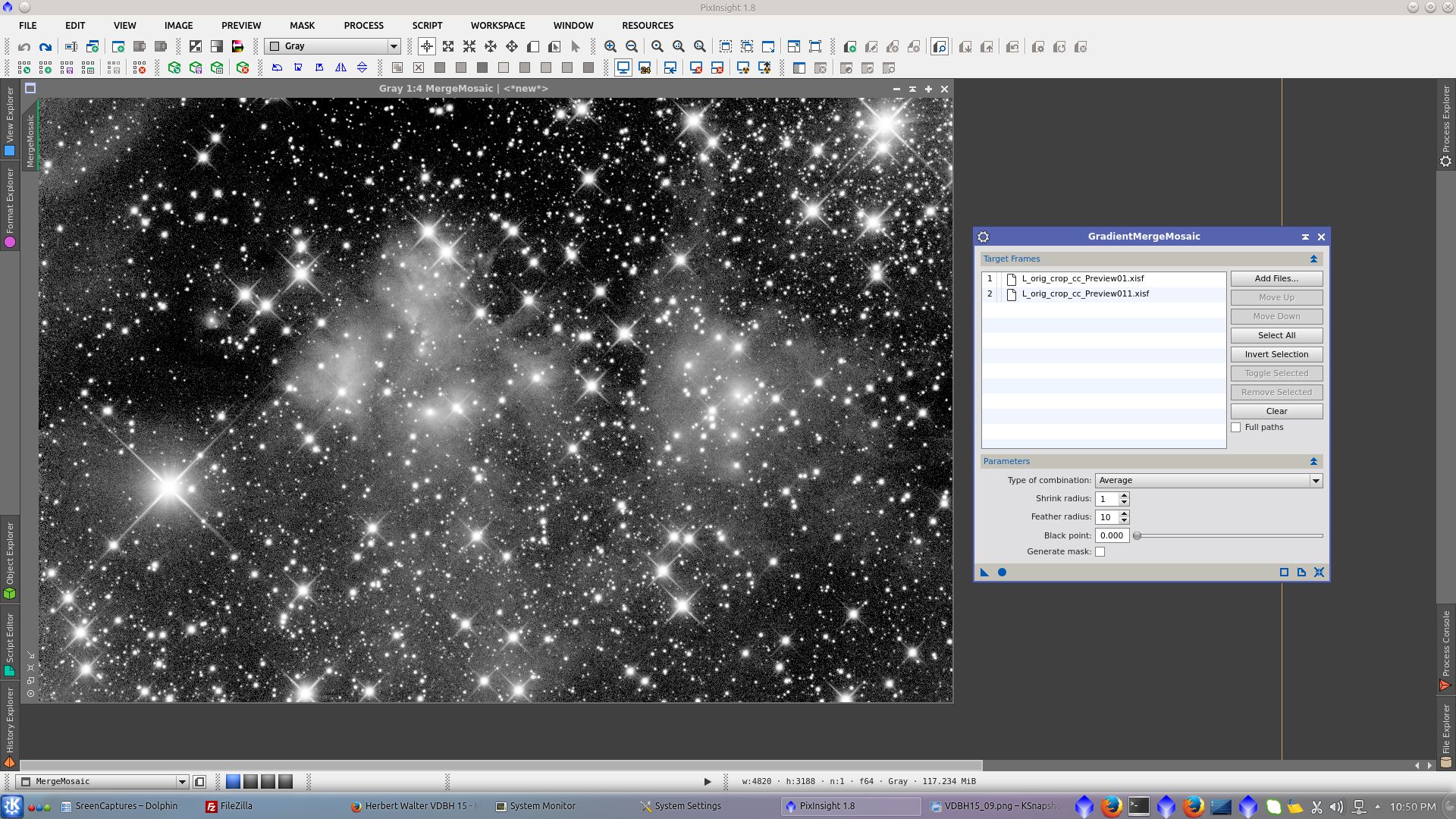
Save both L_previews and use GradientMergeMosaic to reconstruct the L image without the dark line
Following the process of RGB image, first apply BackgroundNeutralization
Color Calibration
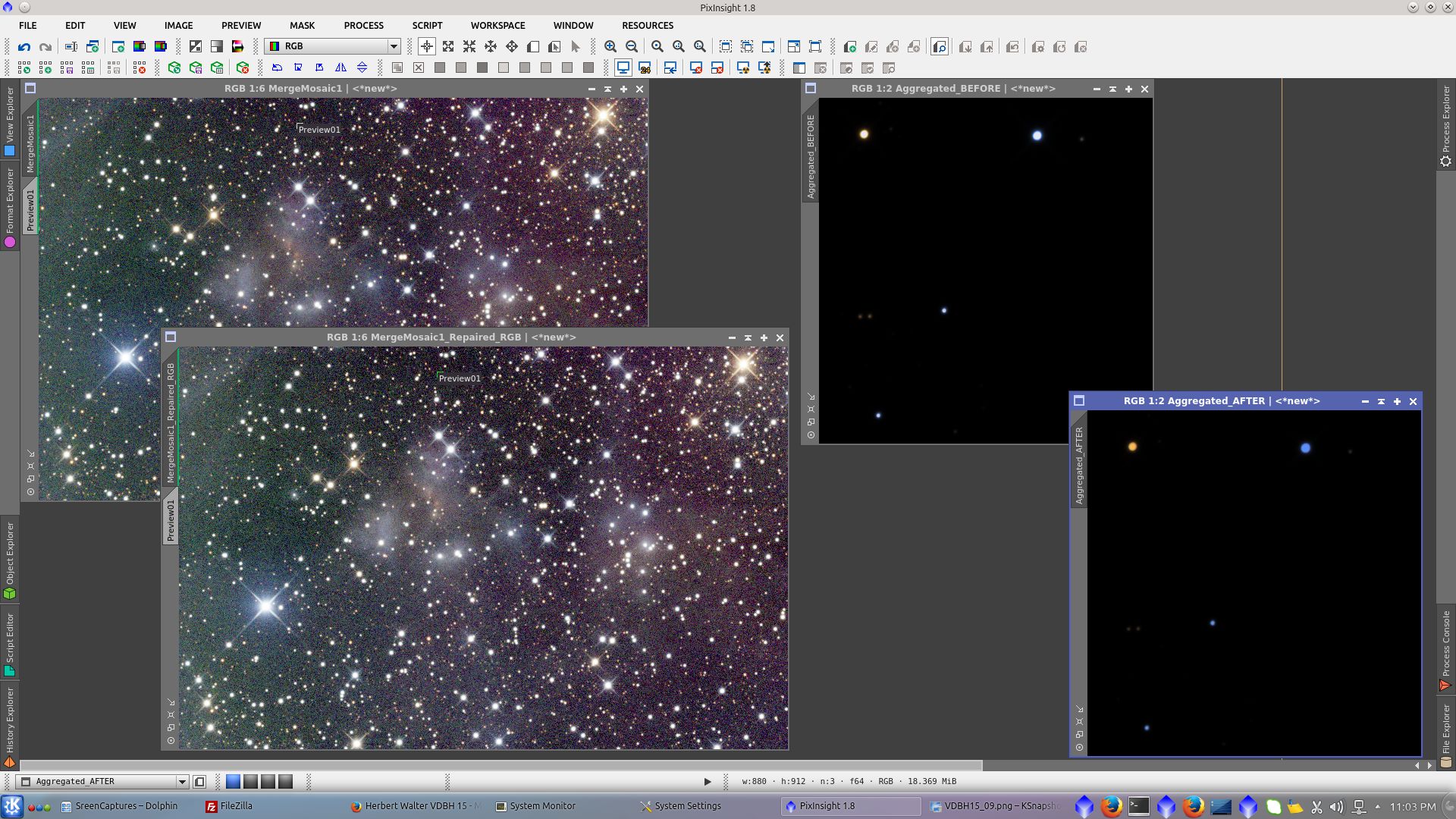
Reparation of the saturated stars cores using RepairedHSVSeparation script
Before and after of the repaired stars when still linear
MaskedStretch on the RGB image. Here starts the non linear post processing of the image and is where more easily can be followed different approaches to the final image
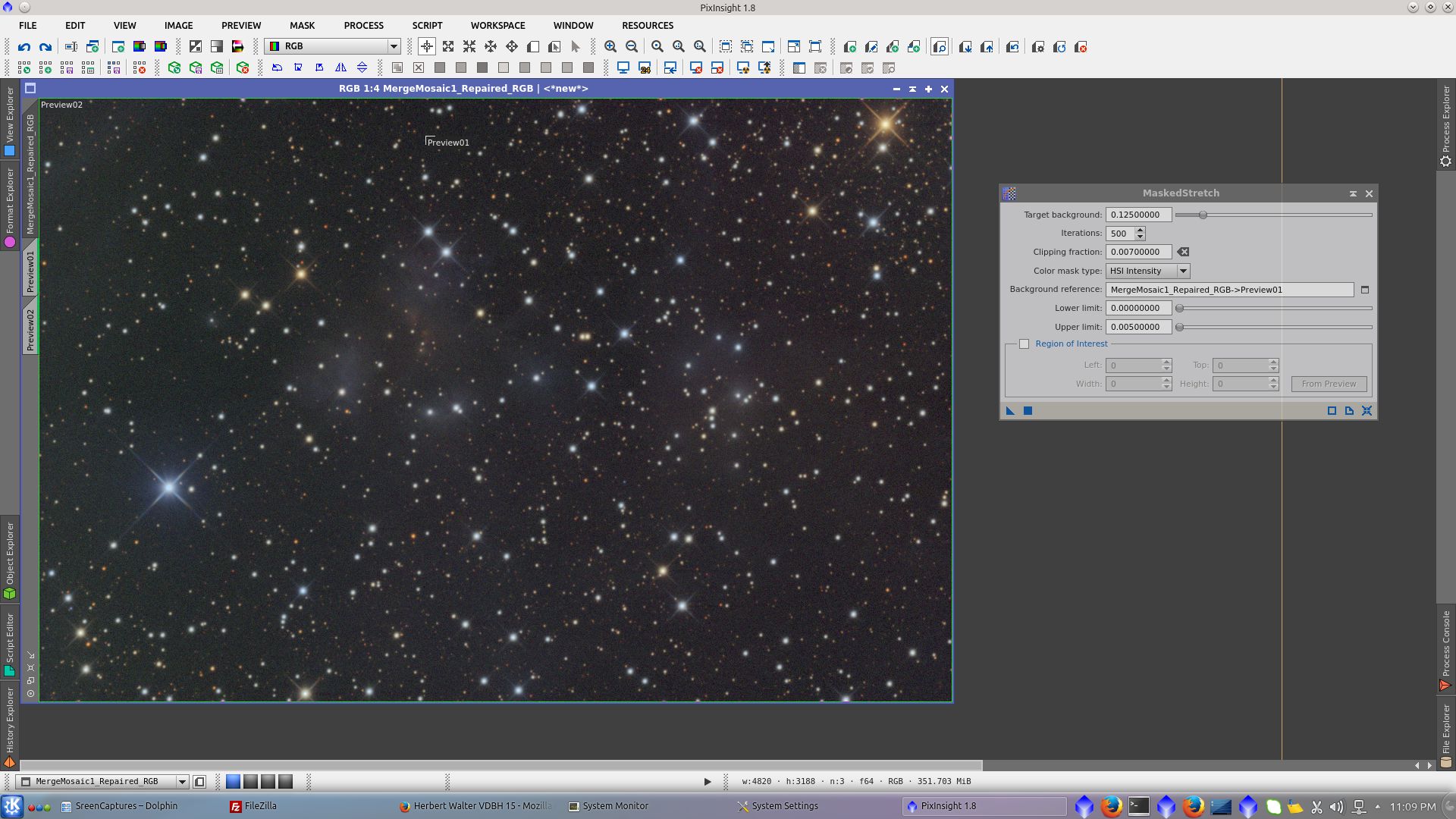
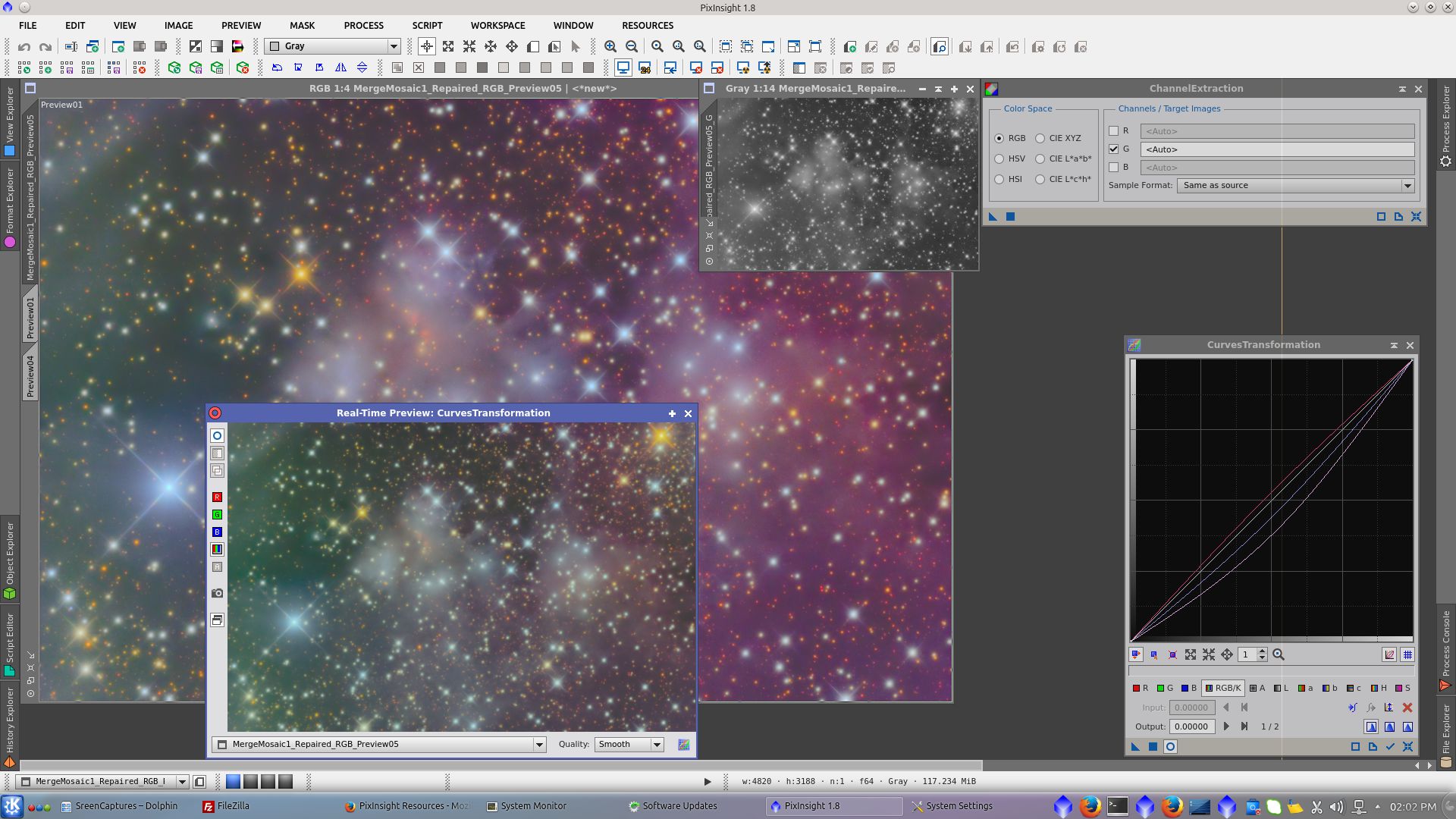
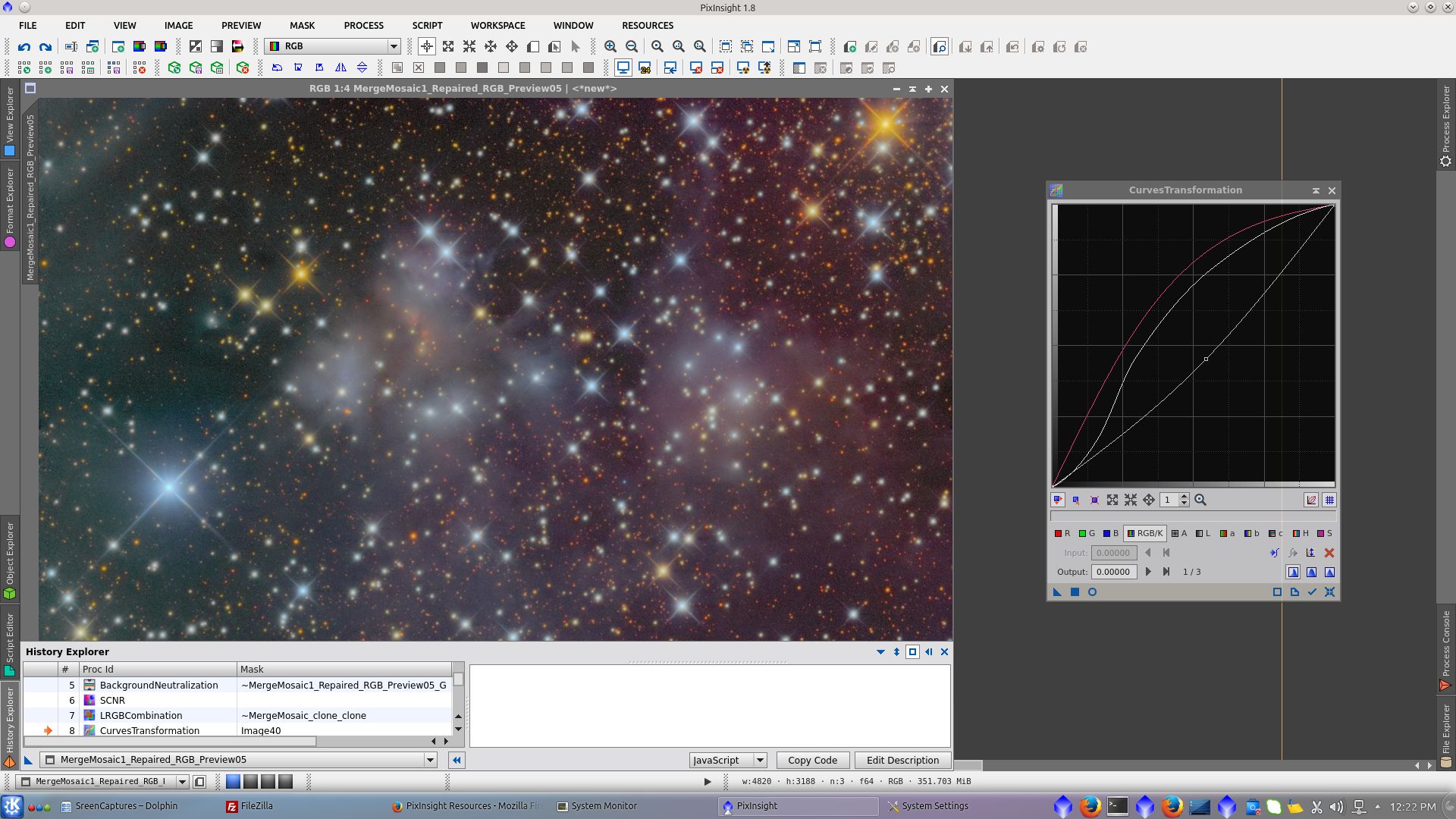
Saturation and color using CurvesTransformation tool
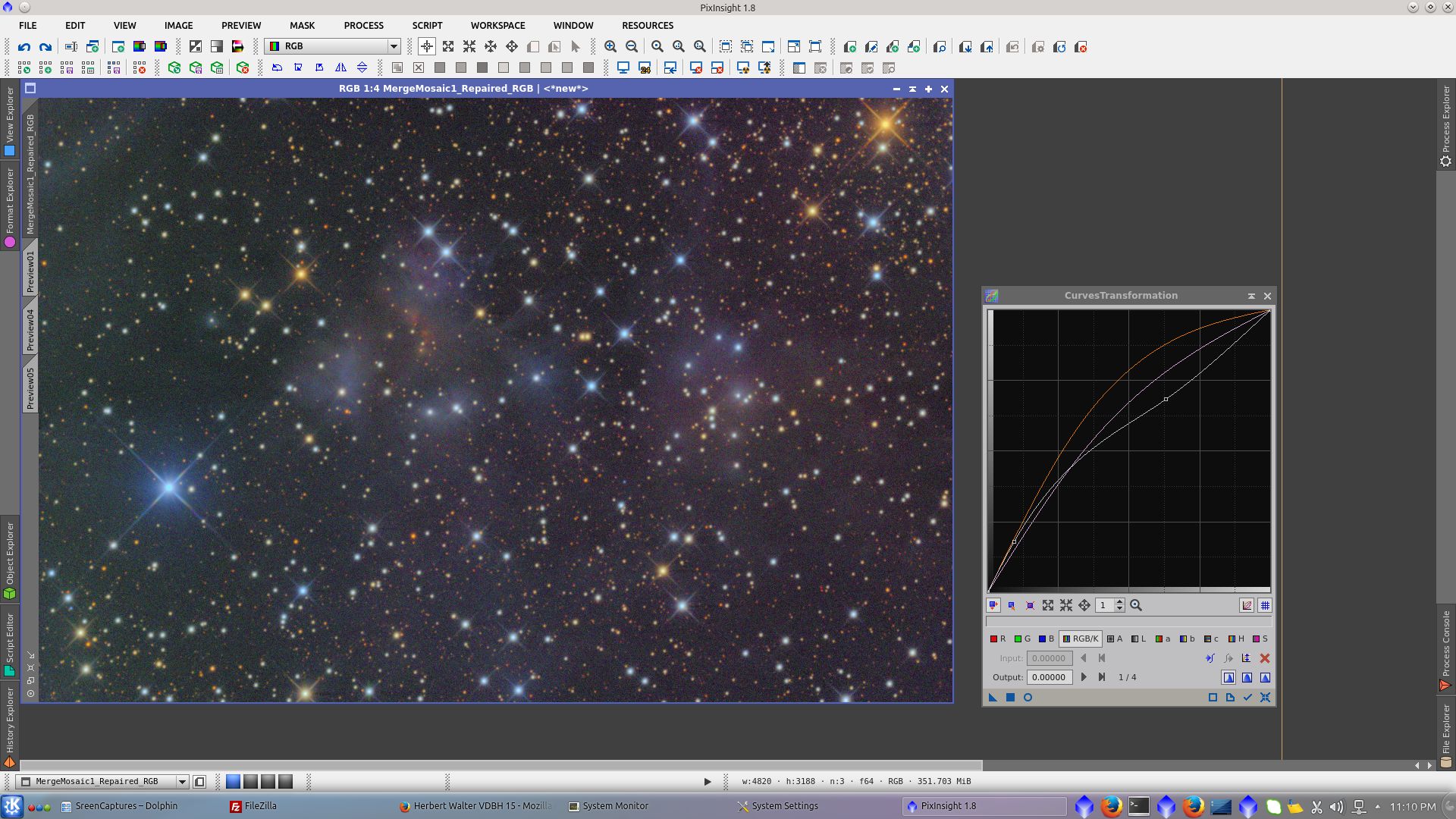
Noise Reduction in Chrominace using ACDNR tool
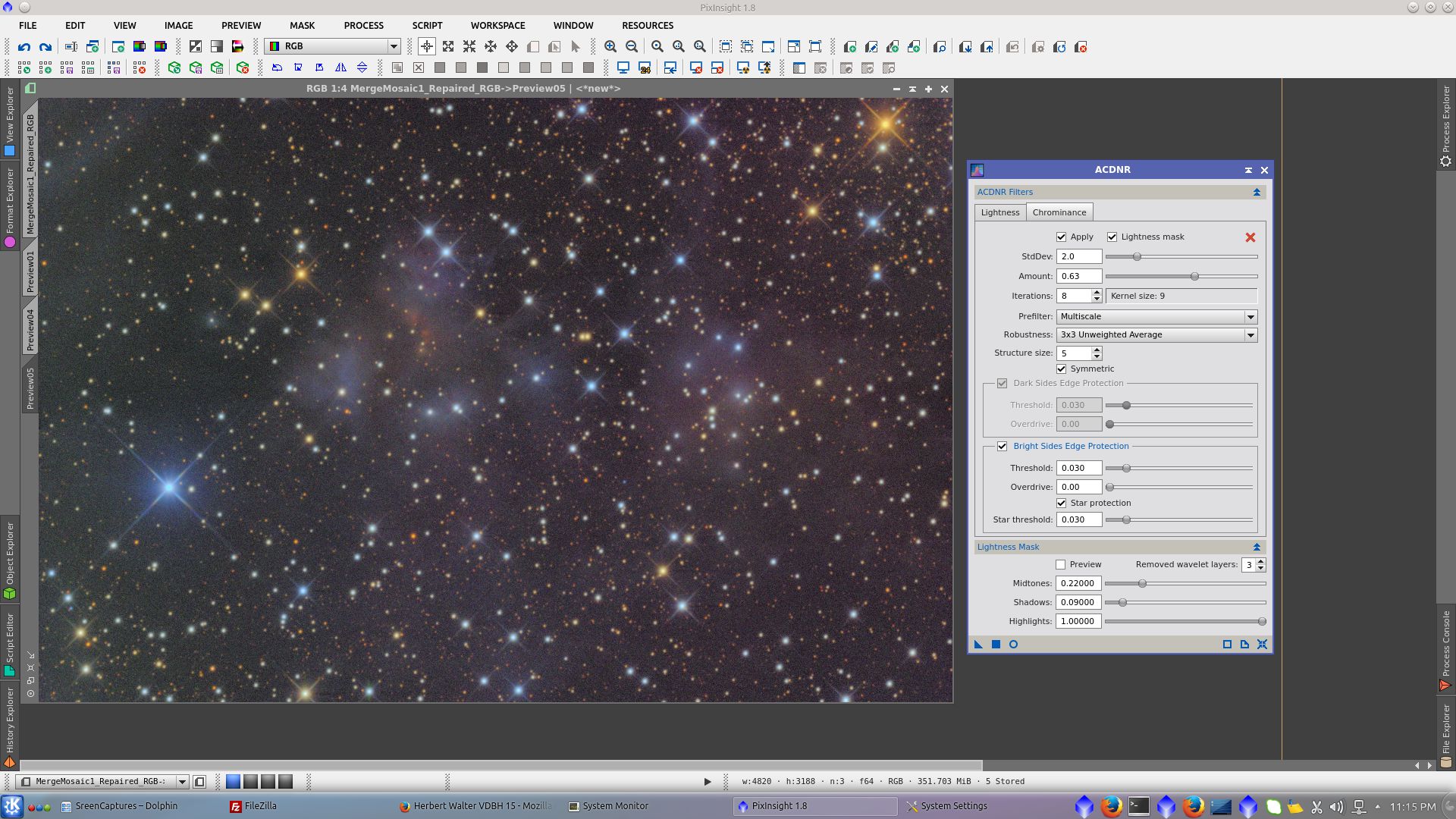
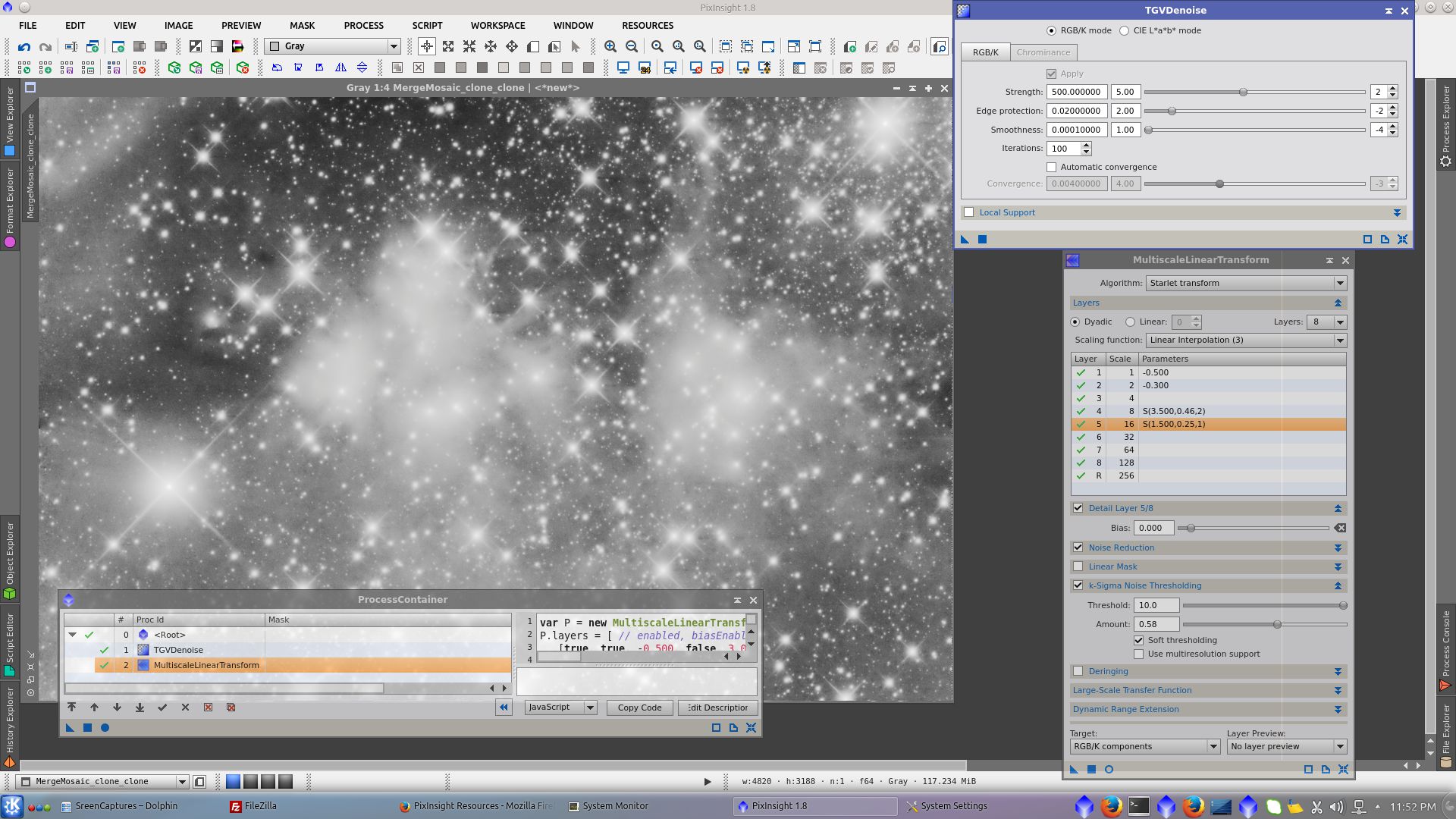
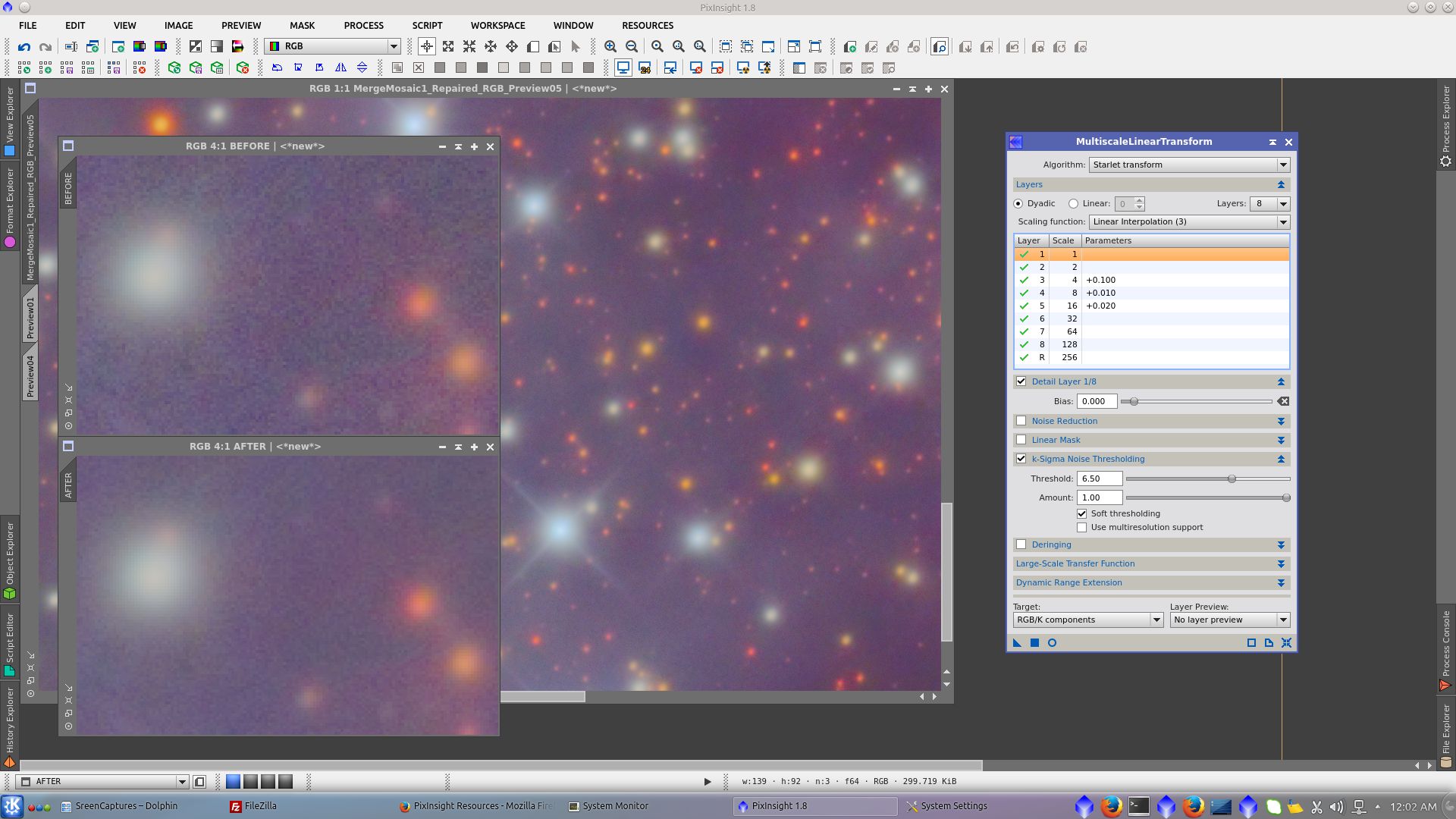
Noise Reduction using k-Sigma Noise Thresholding in MultiscaleLinearTranform tool
ExponentialTransformation
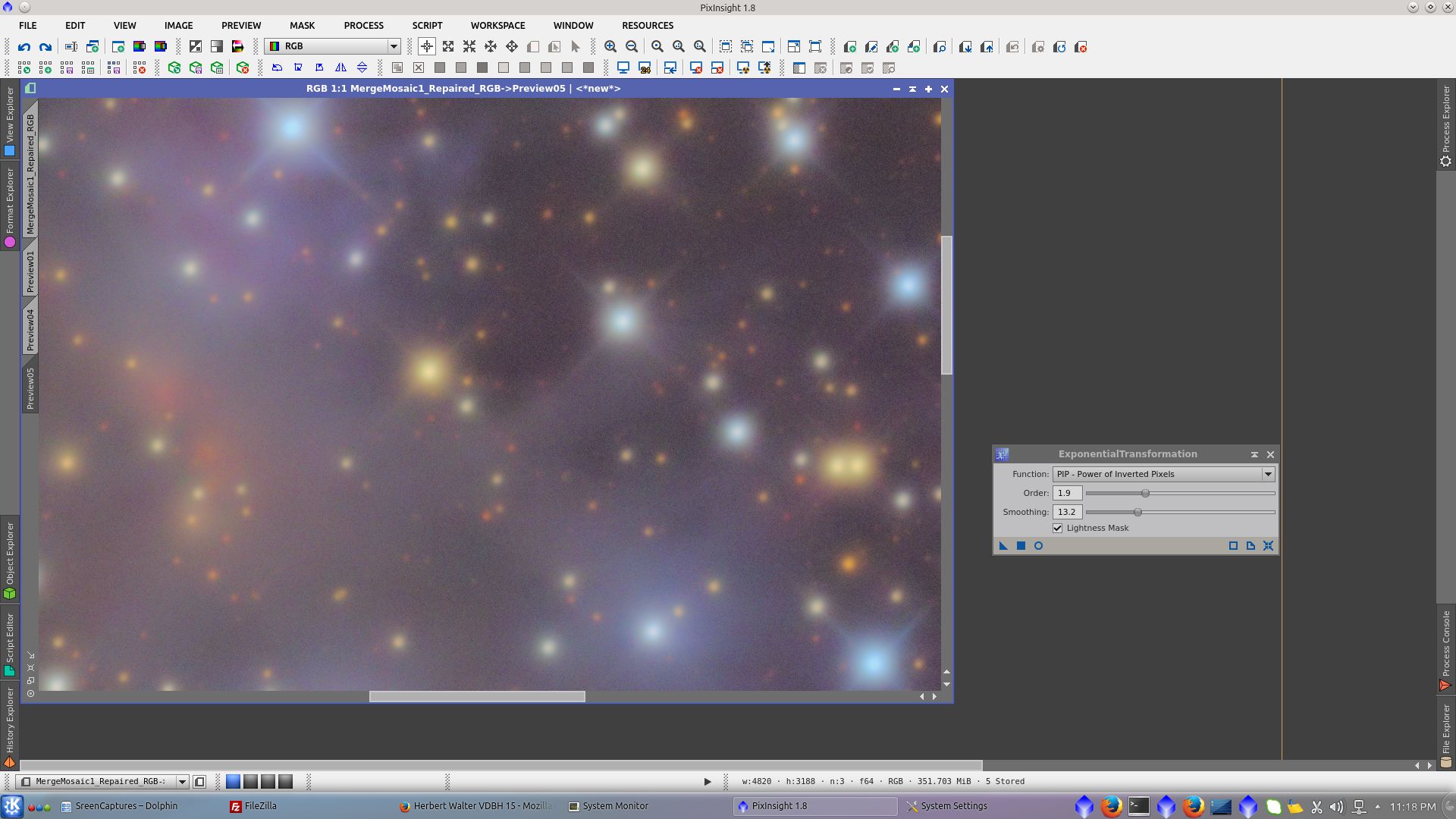
Now continue with L image. Use DynamicPSF to find the PSF for deconvolution
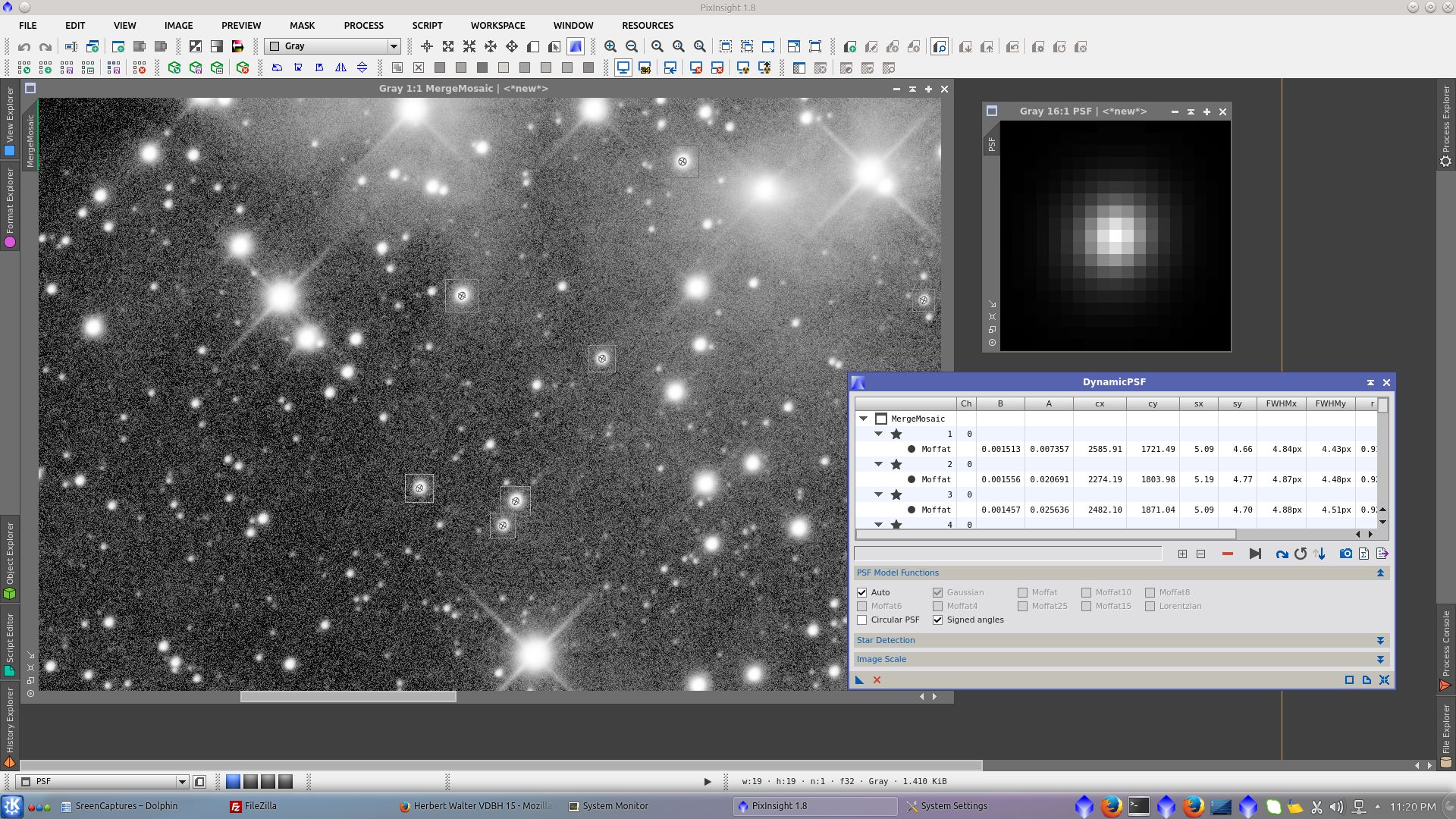
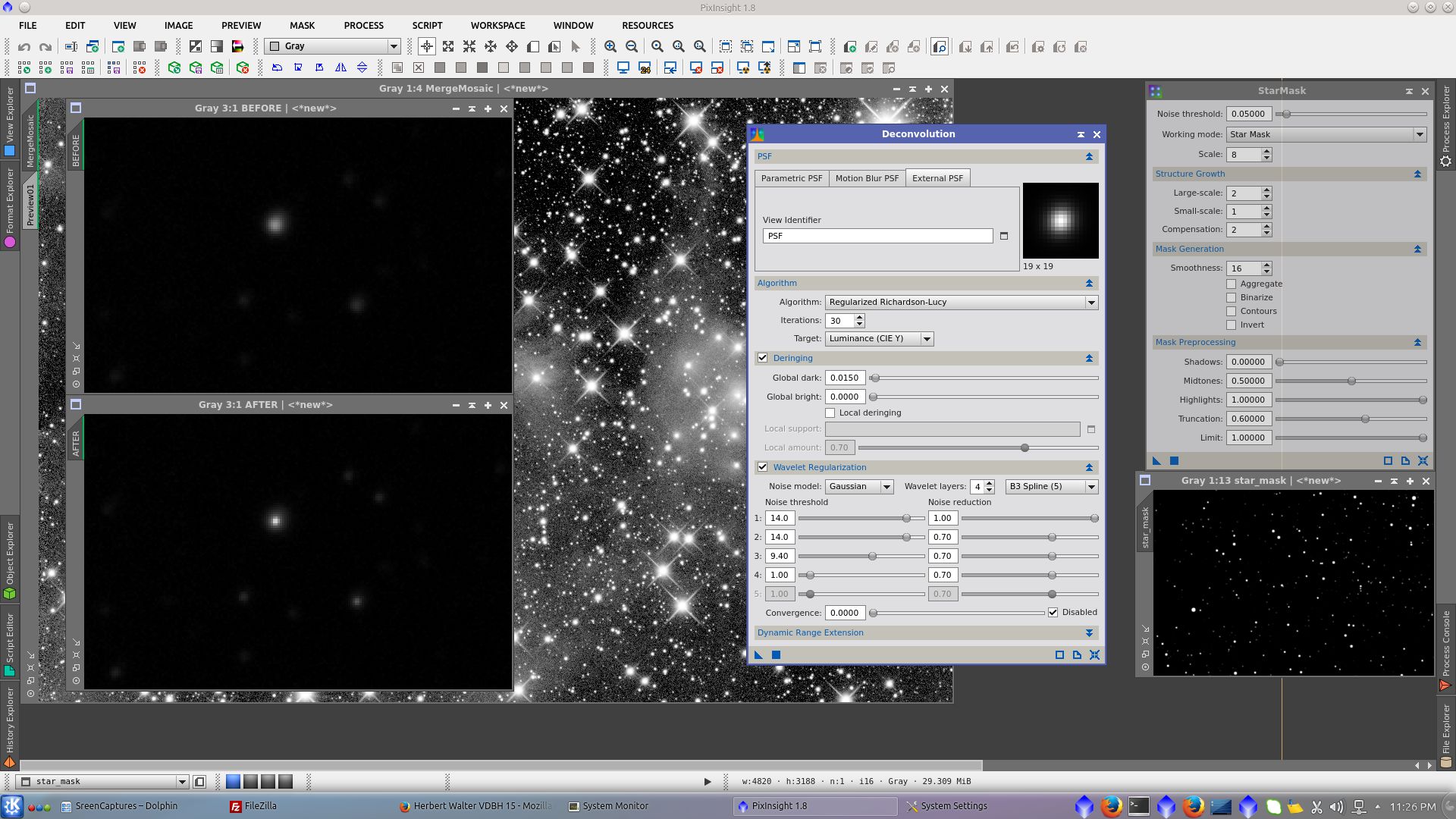
Select the PSF in Deconvolution tool and using StarMask tool generate a starmask to be used protecting stars during deconvolution. Set the correct parameters for Wavelet Regularization to protect the background. See before and after in faint stars.
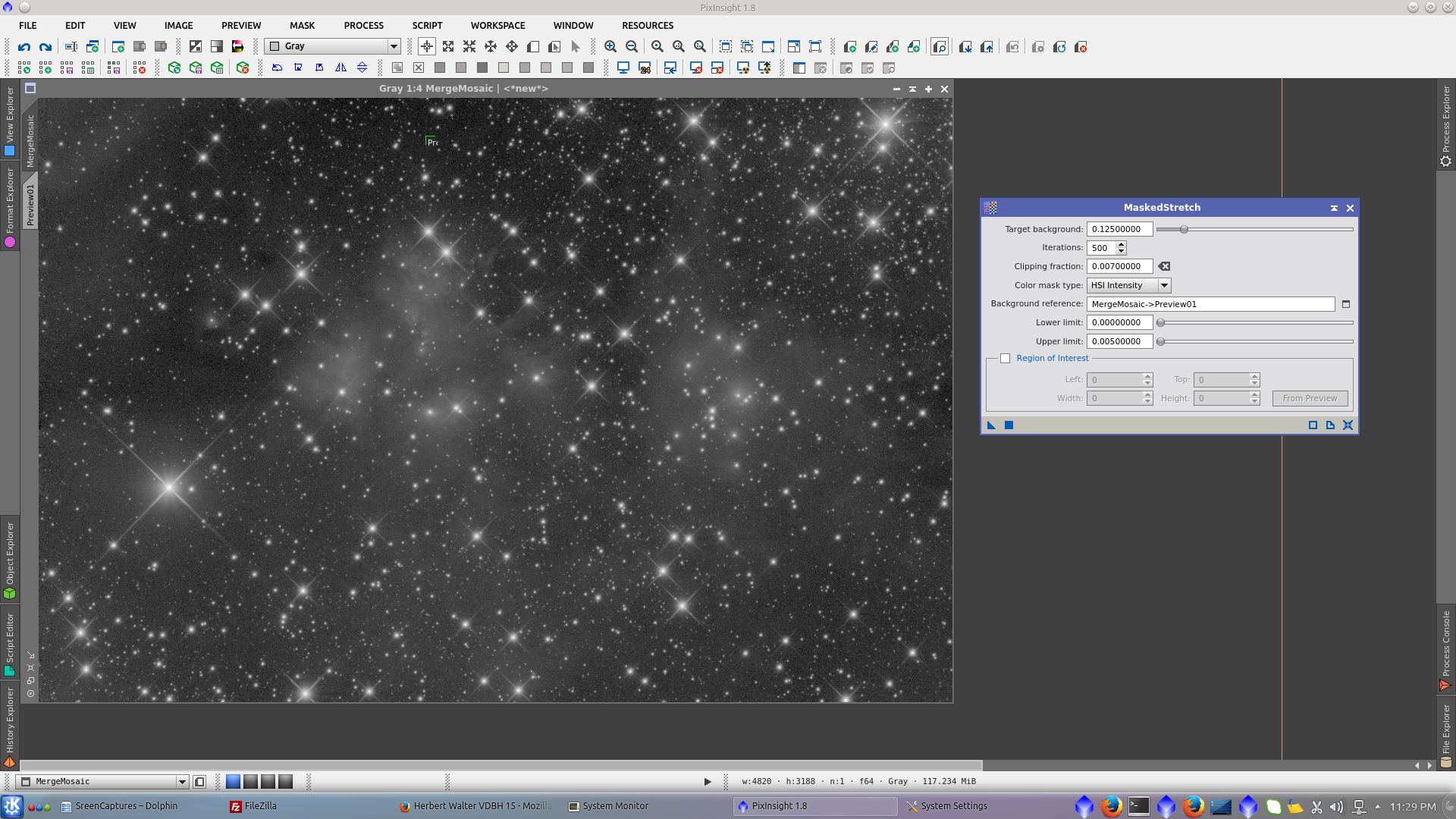
MaskedStretch. Here starts the non linear post processing of the image and is where more easily can be followed different approaches to the final image
Clone L_image and apply AdaptiveStretch to generate a mask with high contrast
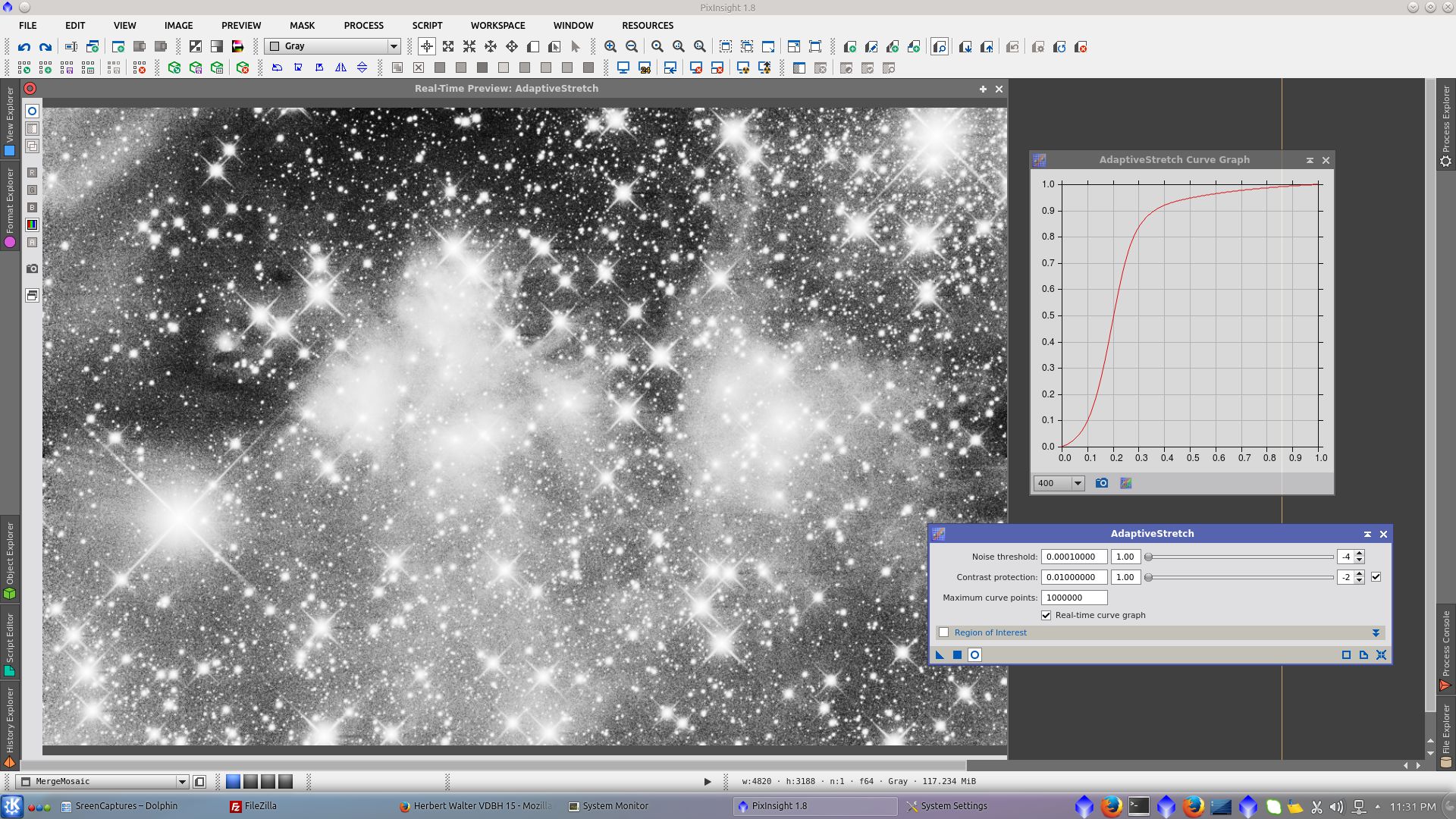
Apply the clone as a mask protecting bright area of the image and use LocalHistogramEqualization to give contrast to the image
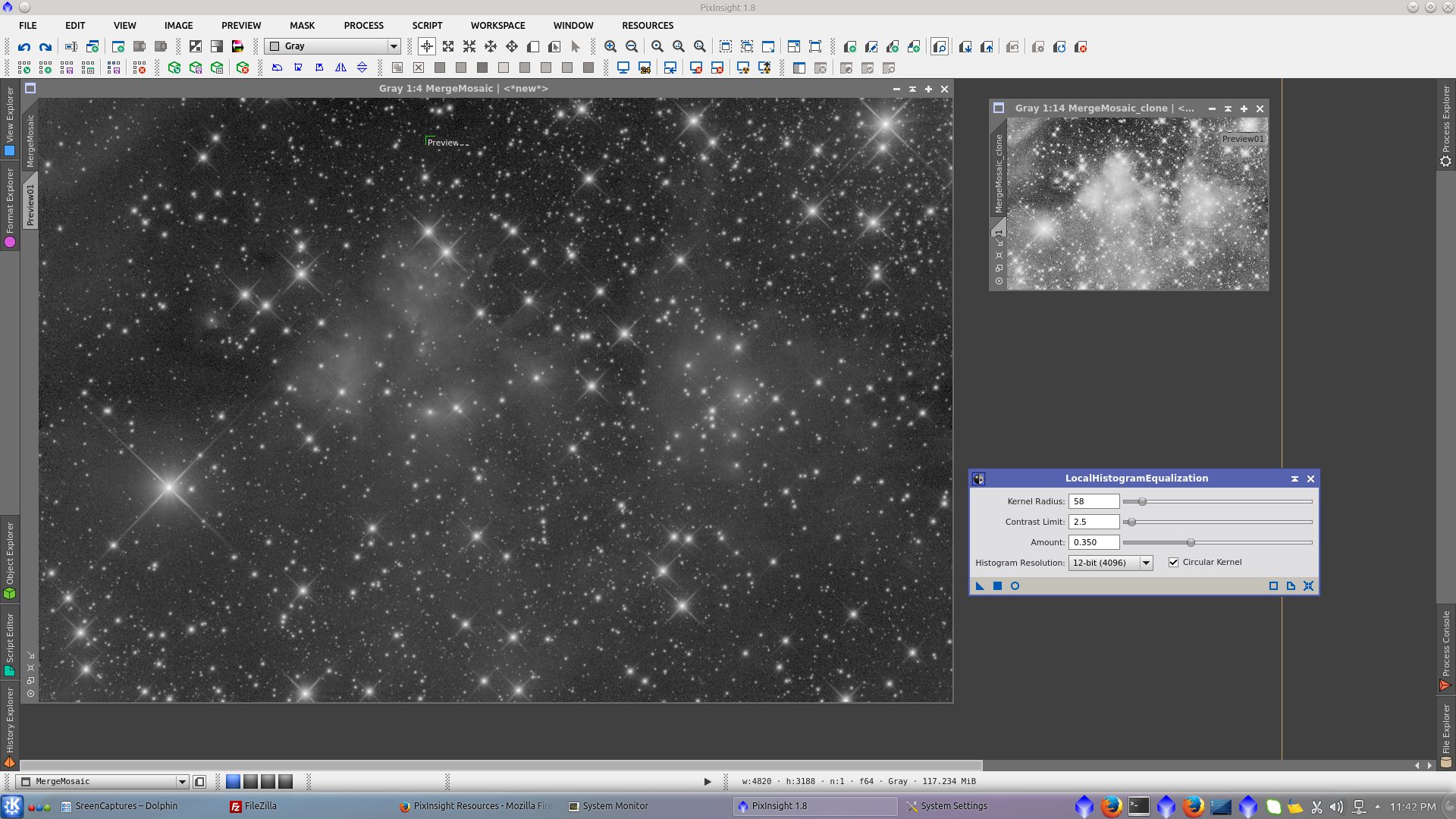
Extract the B channel to be use as mask and protecting bright areas of the image adjust CIE c using Blue channel as Reference in InterChannelCurves
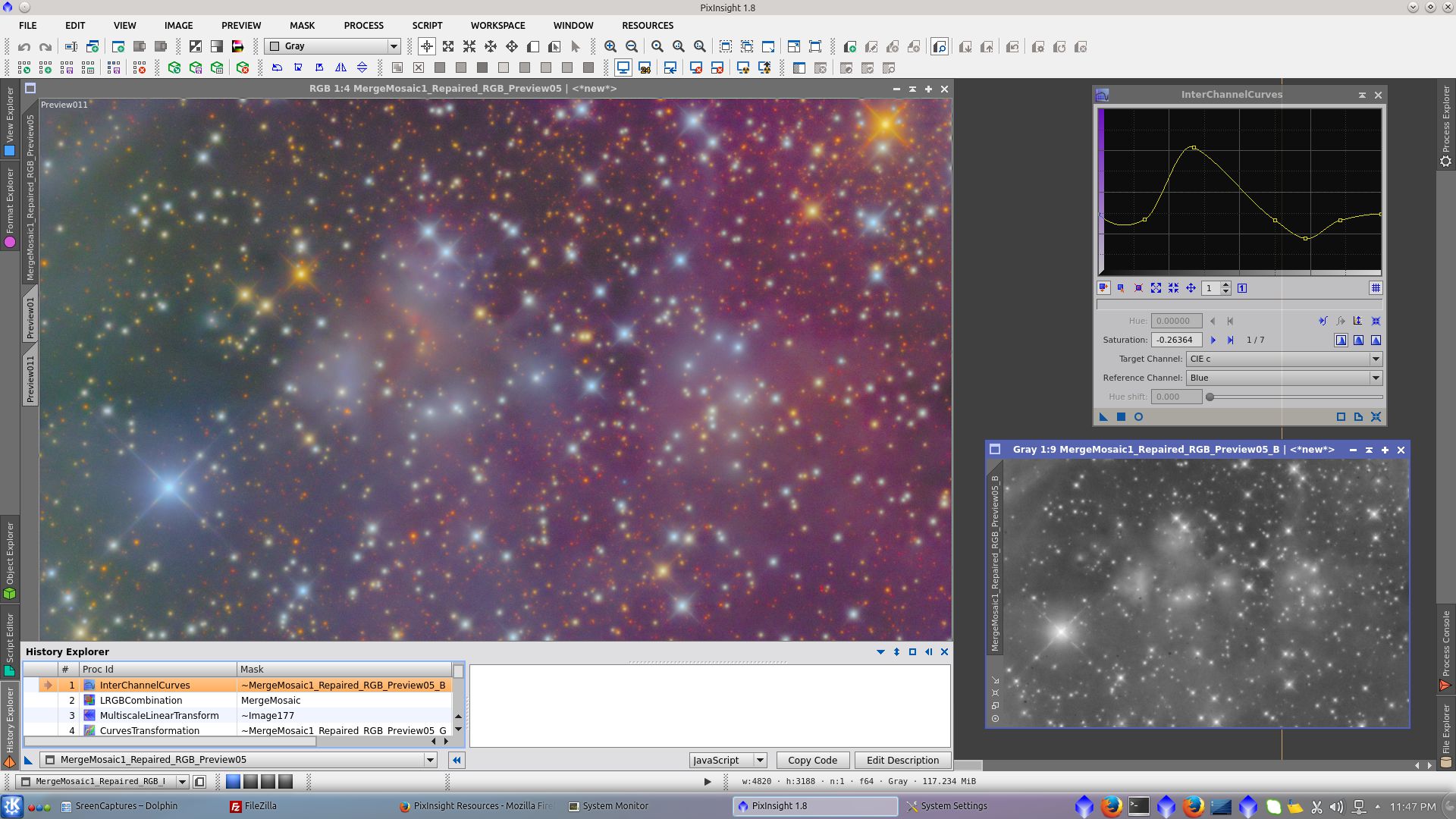
Before adding L to RGB, clone L_image and apply noise reduction using TGVDenoise and MultiscaleLinearTransform
Add L To RGB image
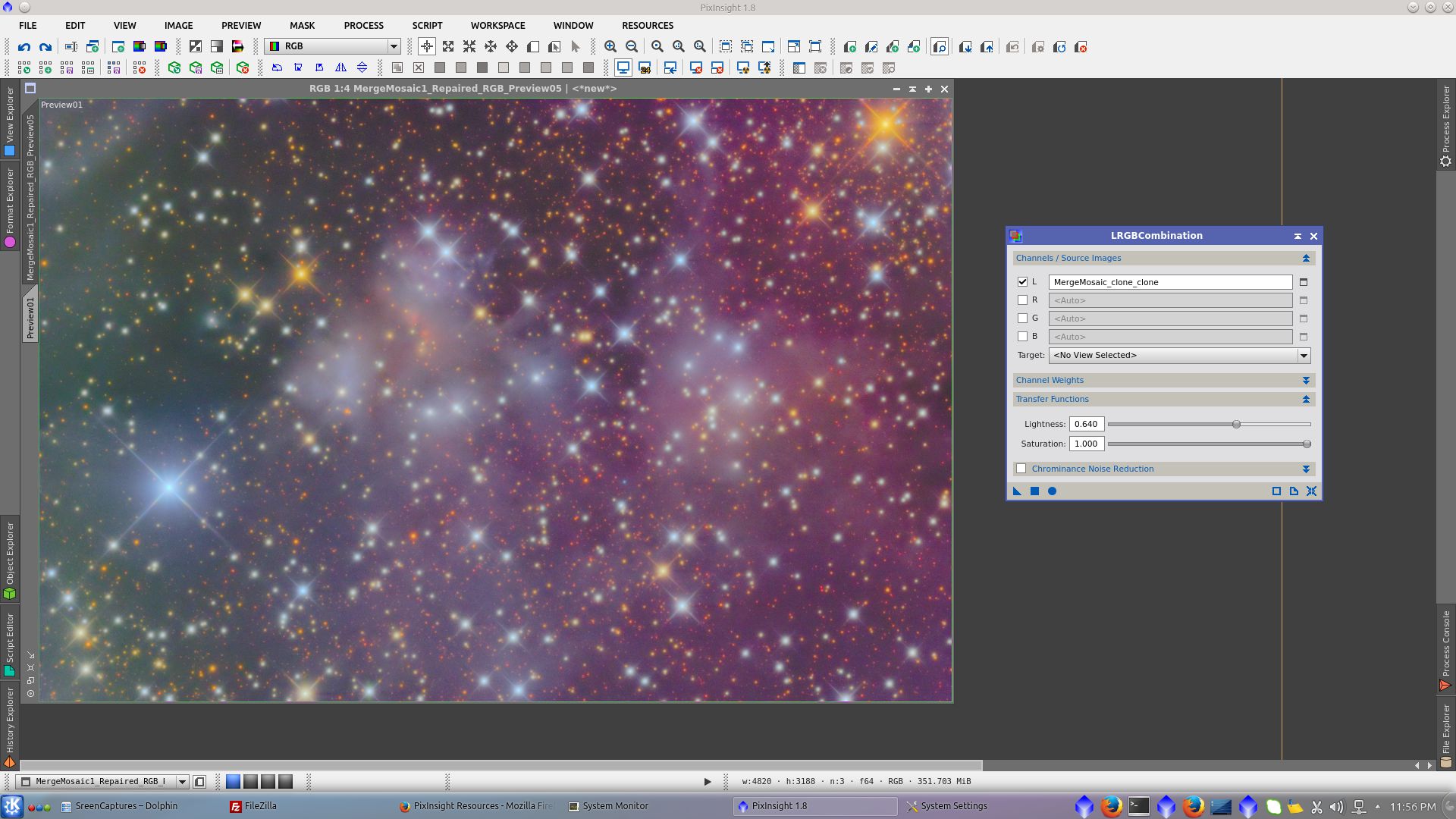
Generate a mask to protect stars and background using PixelMath to subtract the previously created starmask from L image
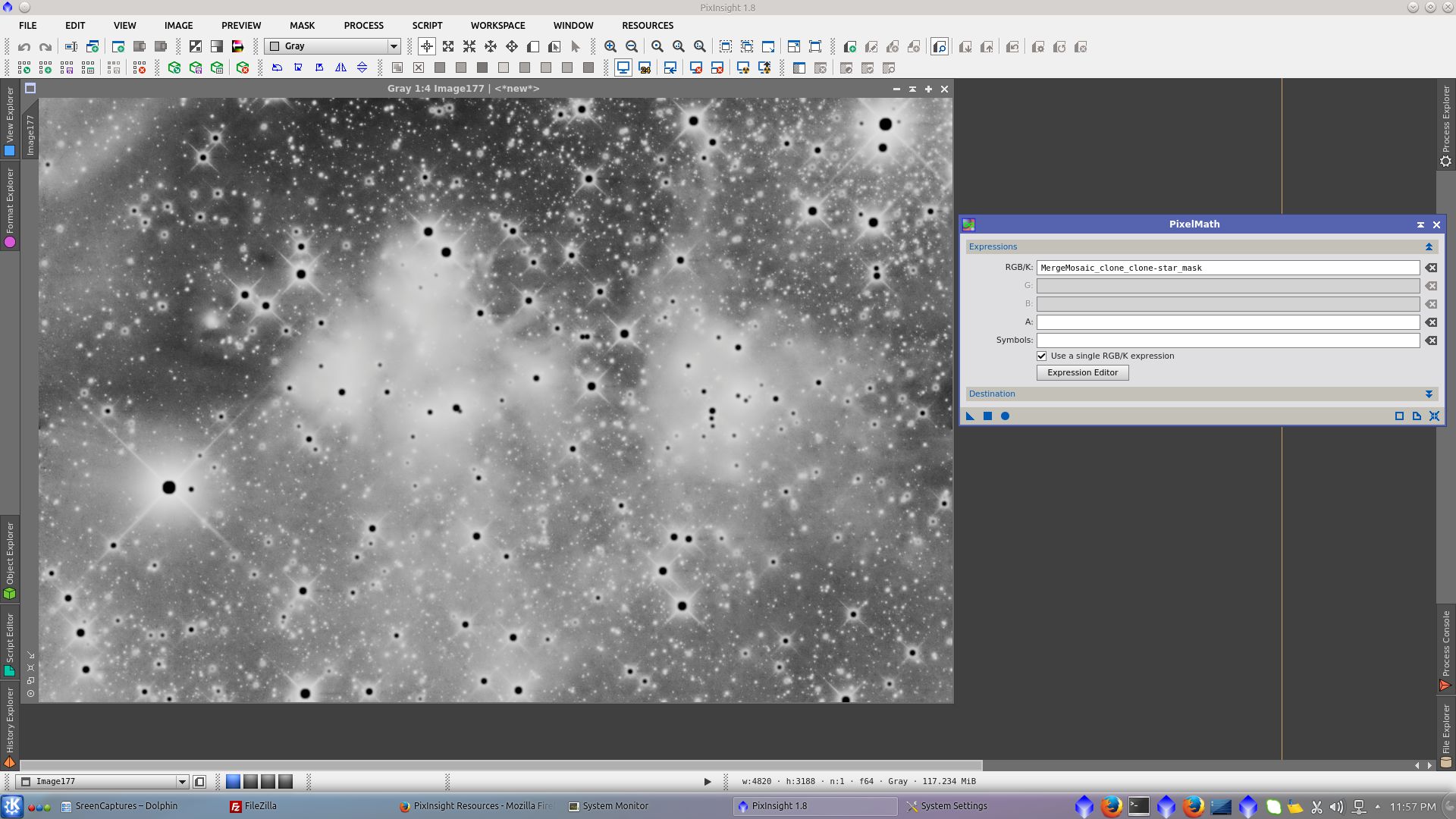
Use MultiscaleLinearTransform to noise reduction using k-sigma Noise Thresholding and protecting bright areas increasing Bias in layers of 4,8 and 16 pixels
Extract _G channel using ChannelExtraction tool to be used as mask protecting the nebulae while decreasing saturation in the background and adjusting a and b channels
BackgroundNeutralization tool to equalize the values of the background still protecting with _G channel
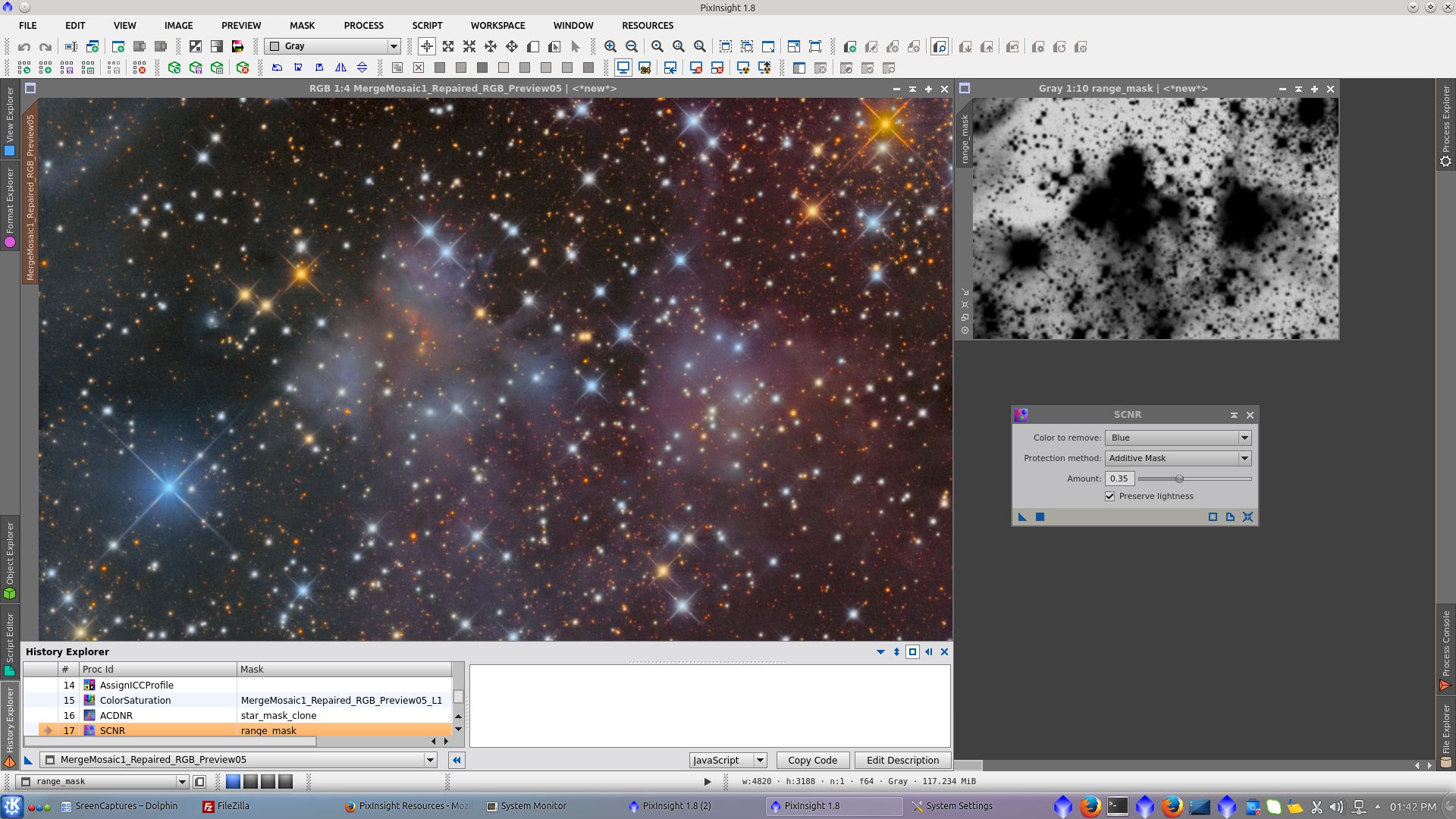
SCNR to reduce green cast. Apply without mask
To recover a more sharp look of the background add more L from the original L (MergeMosaic) but protecting L with the stretched Lmask.
Generate a mask to work over the background. Extract RGB channels and subtract R-G and B-G from the new image
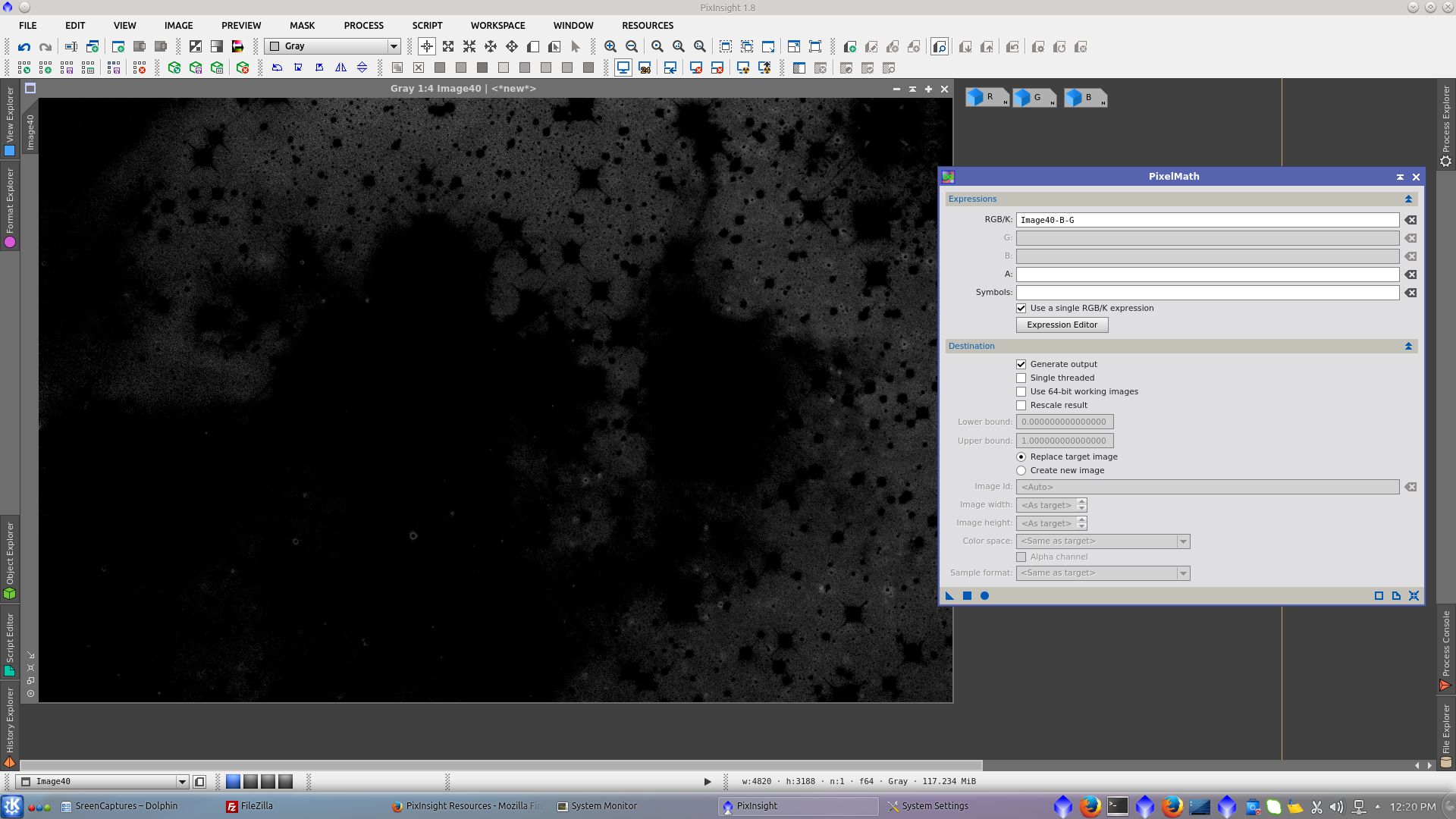
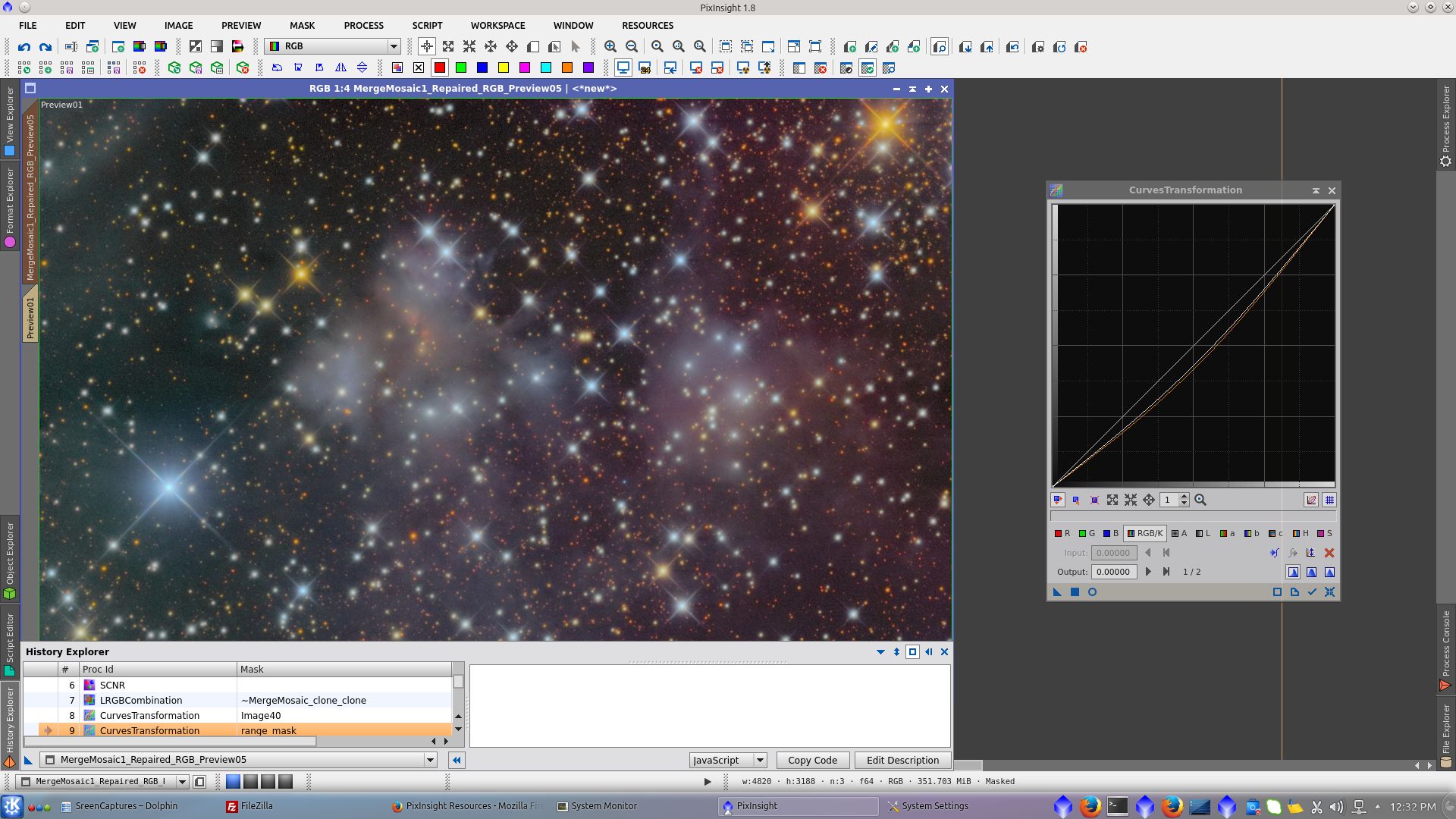
Adjust Cuves protecting the nebula with image40
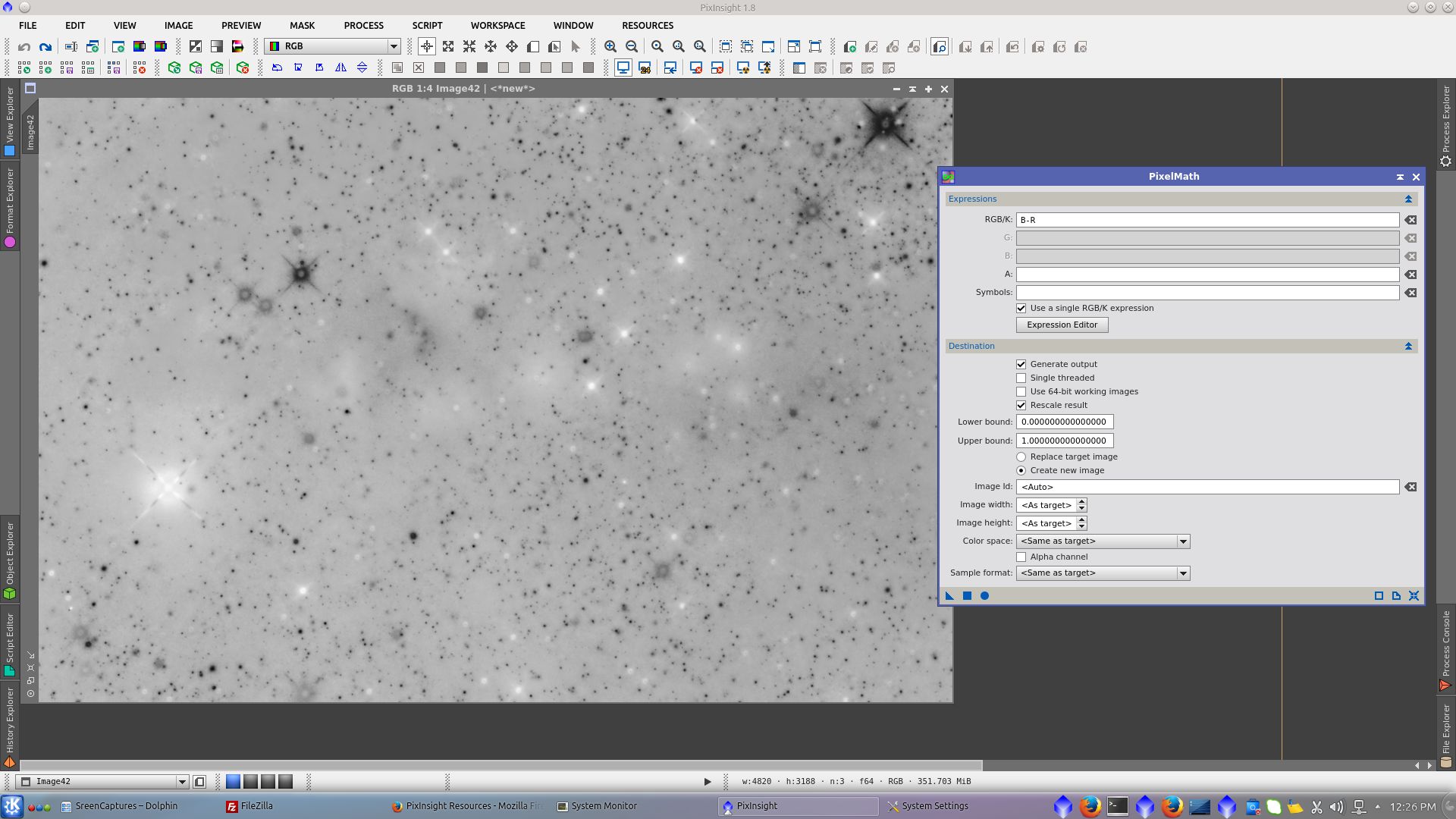
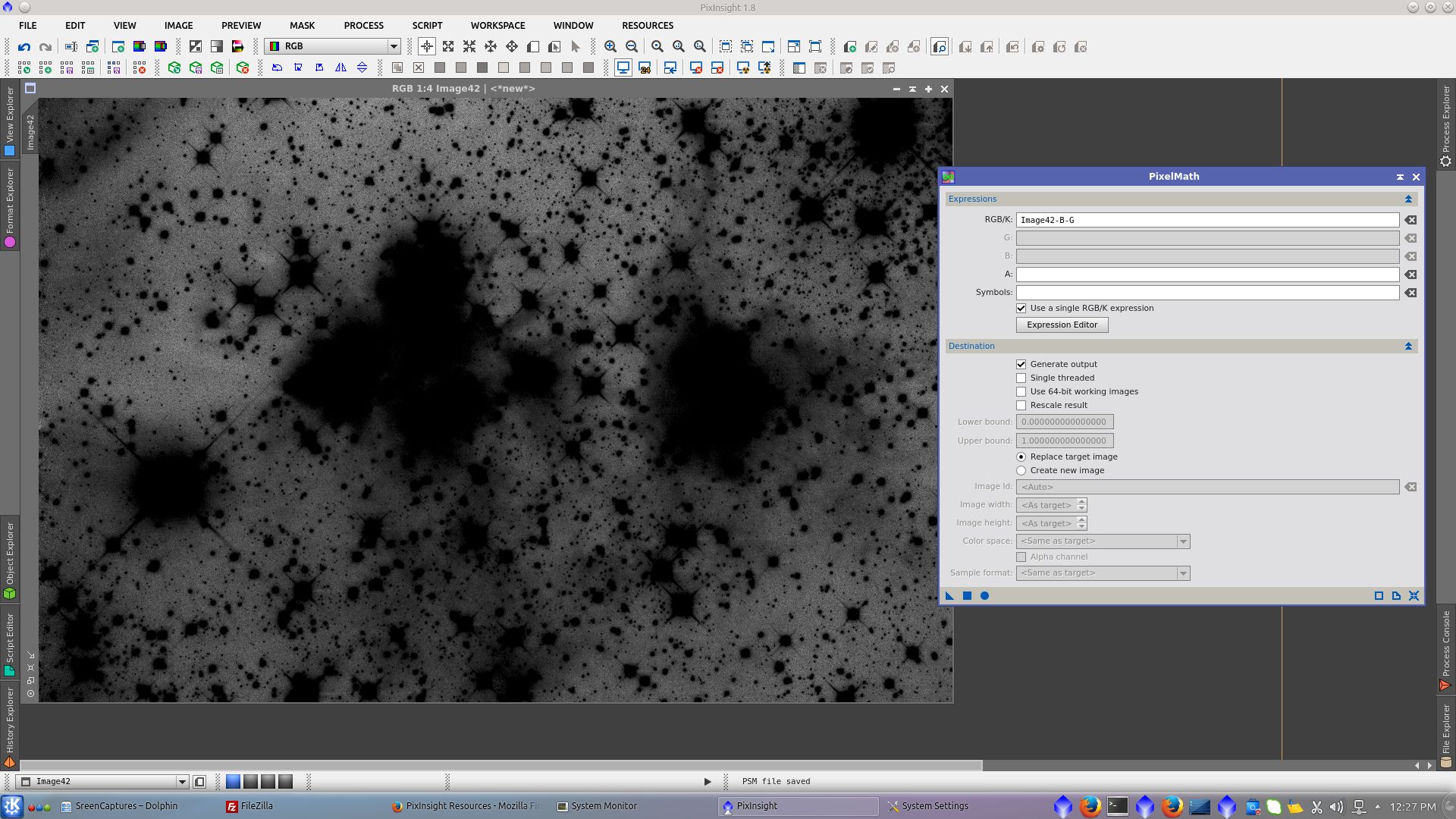
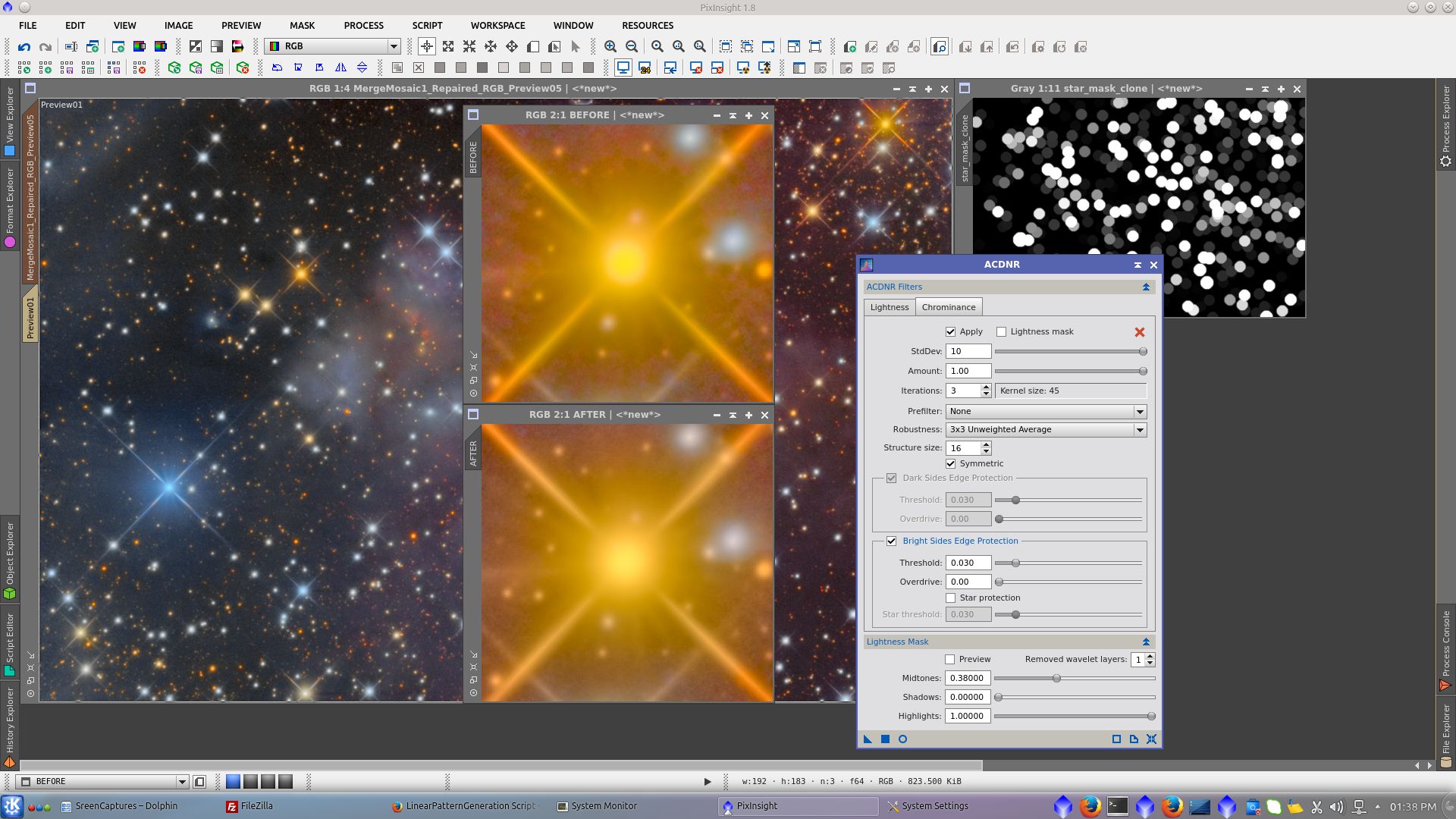
Generate a mask to work over the background. Extract RGB channels and subtract B-R and B-G from the new image and finally use RangeSelection tool to generate a range_mask over it
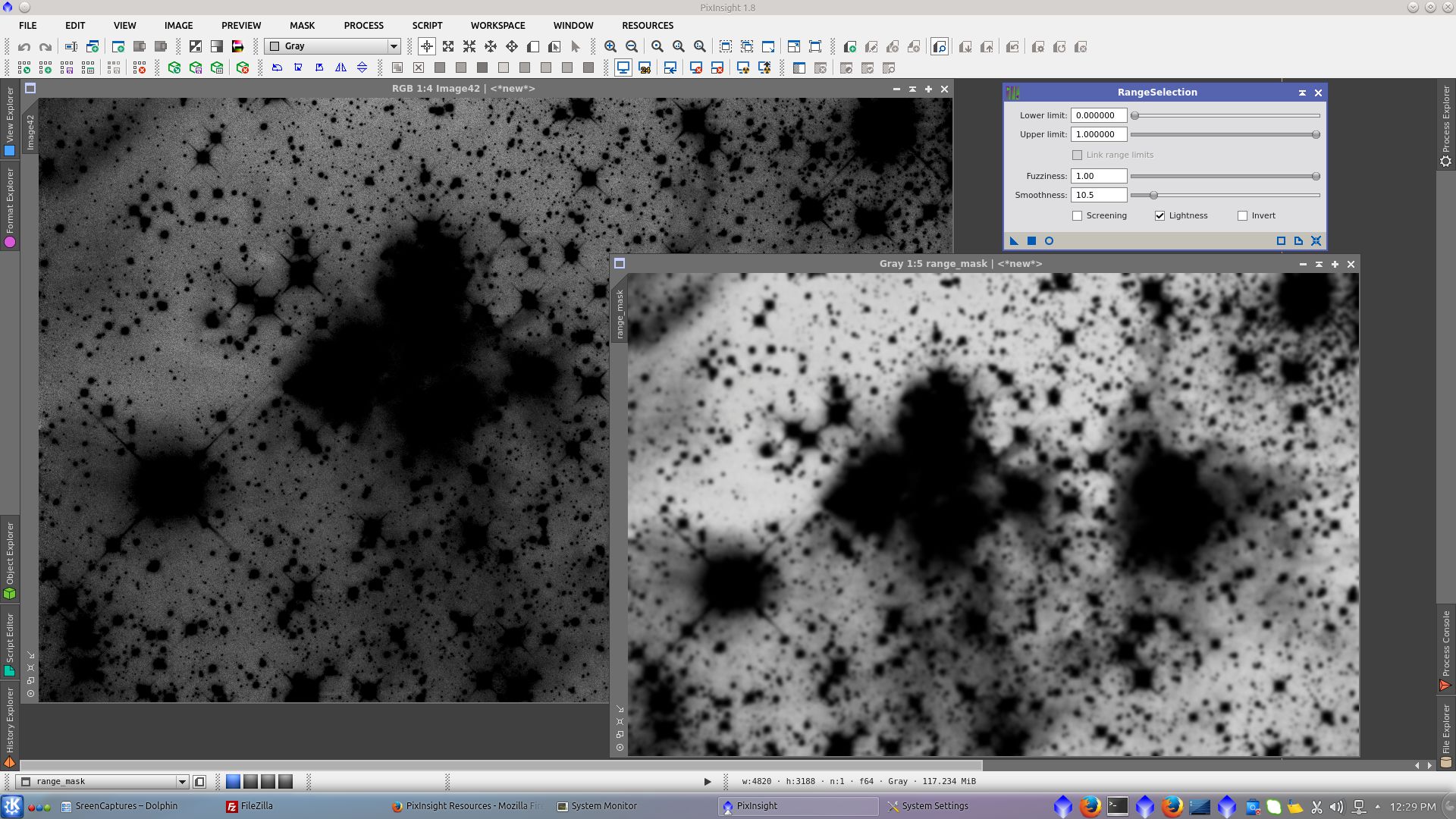
Adjust Cuves protecting the nebula with range_mask
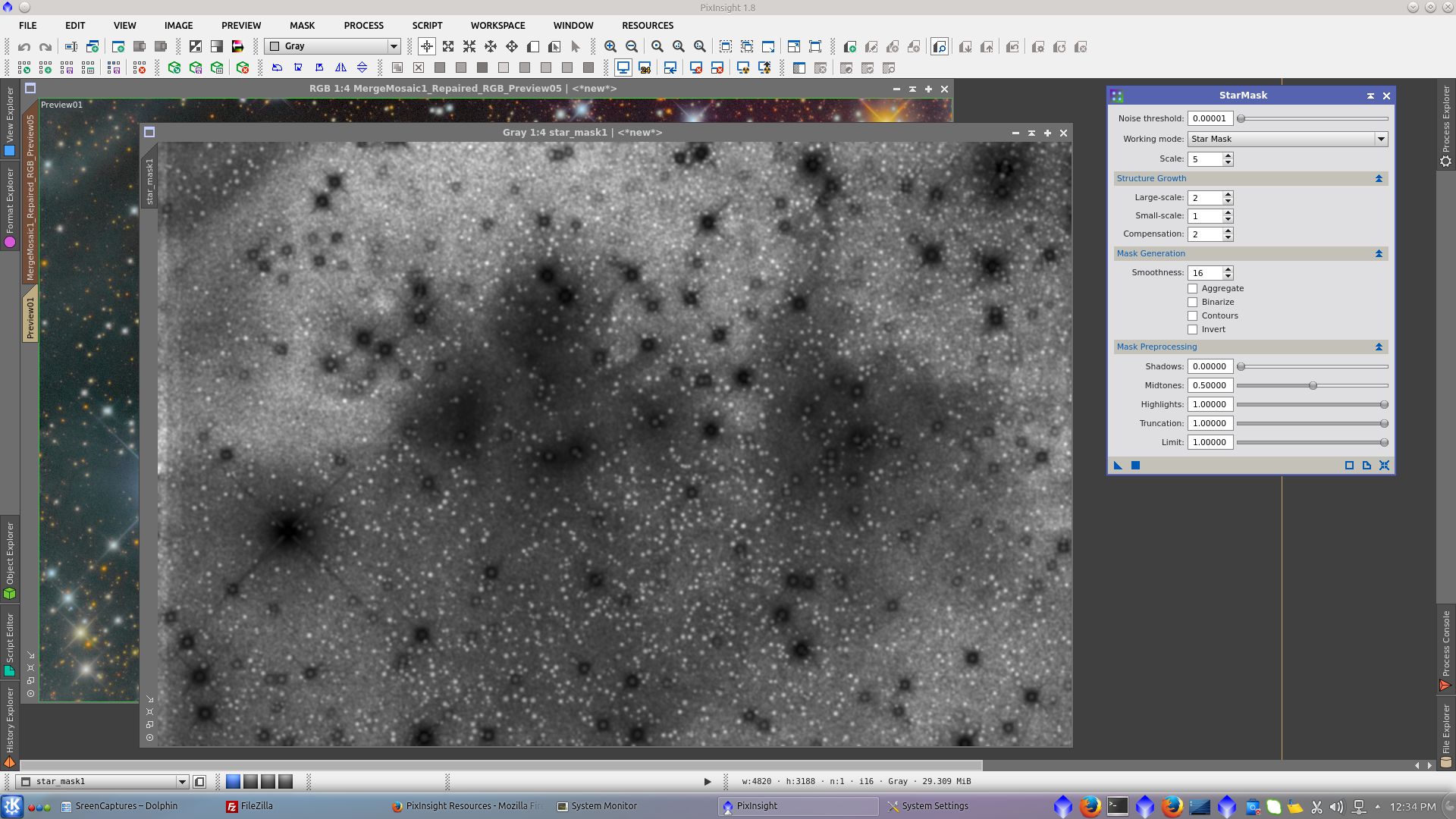
Create a starmask using StarMask tool to be used with MorphologialTransformation tool
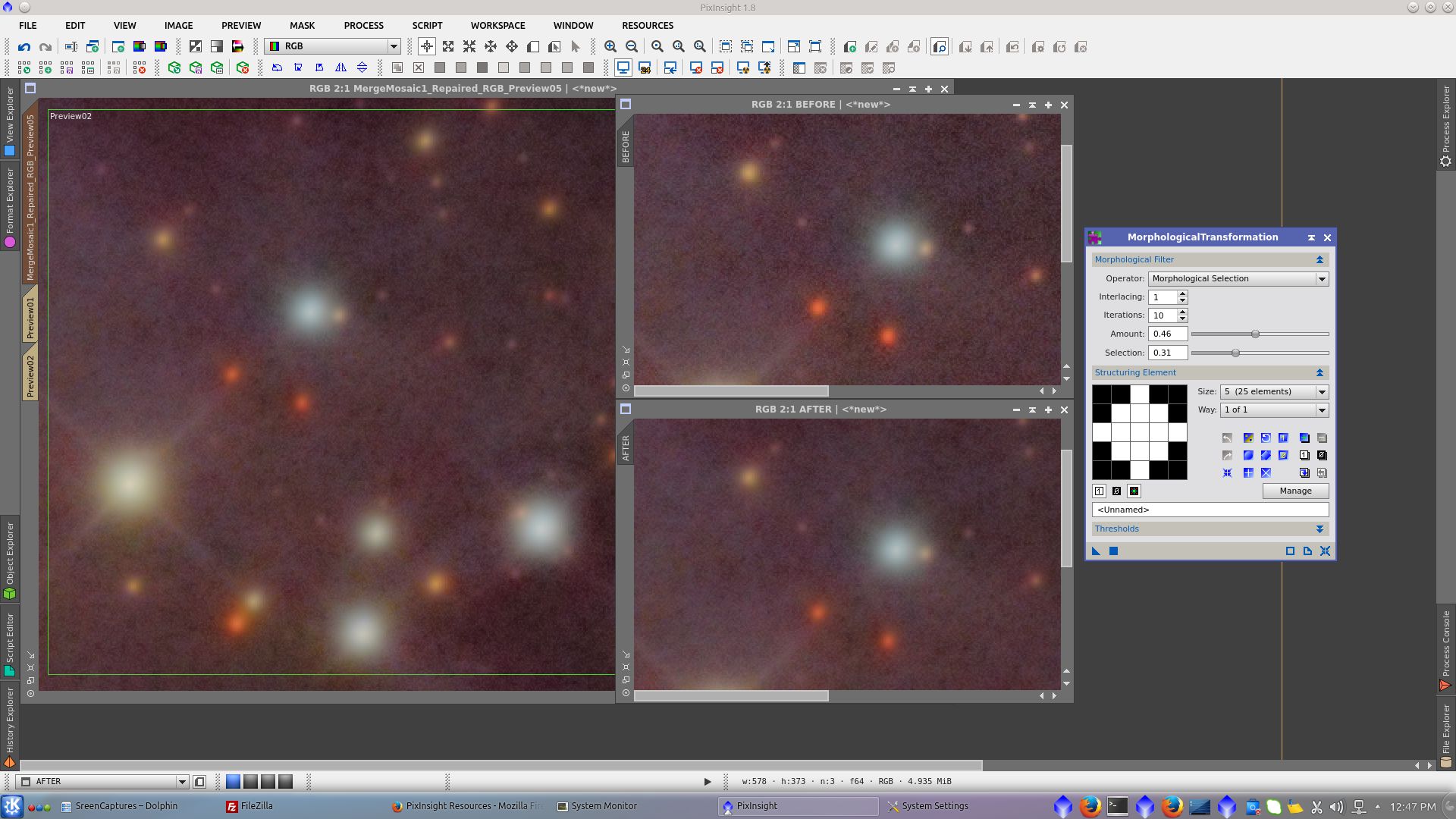
Use Morphological Selection to noise reduction and reduction of stars protecting with starmask
Extract L and use it to protect background and apply HDRMultiscaleTrasform to compress the dynamic range of the image
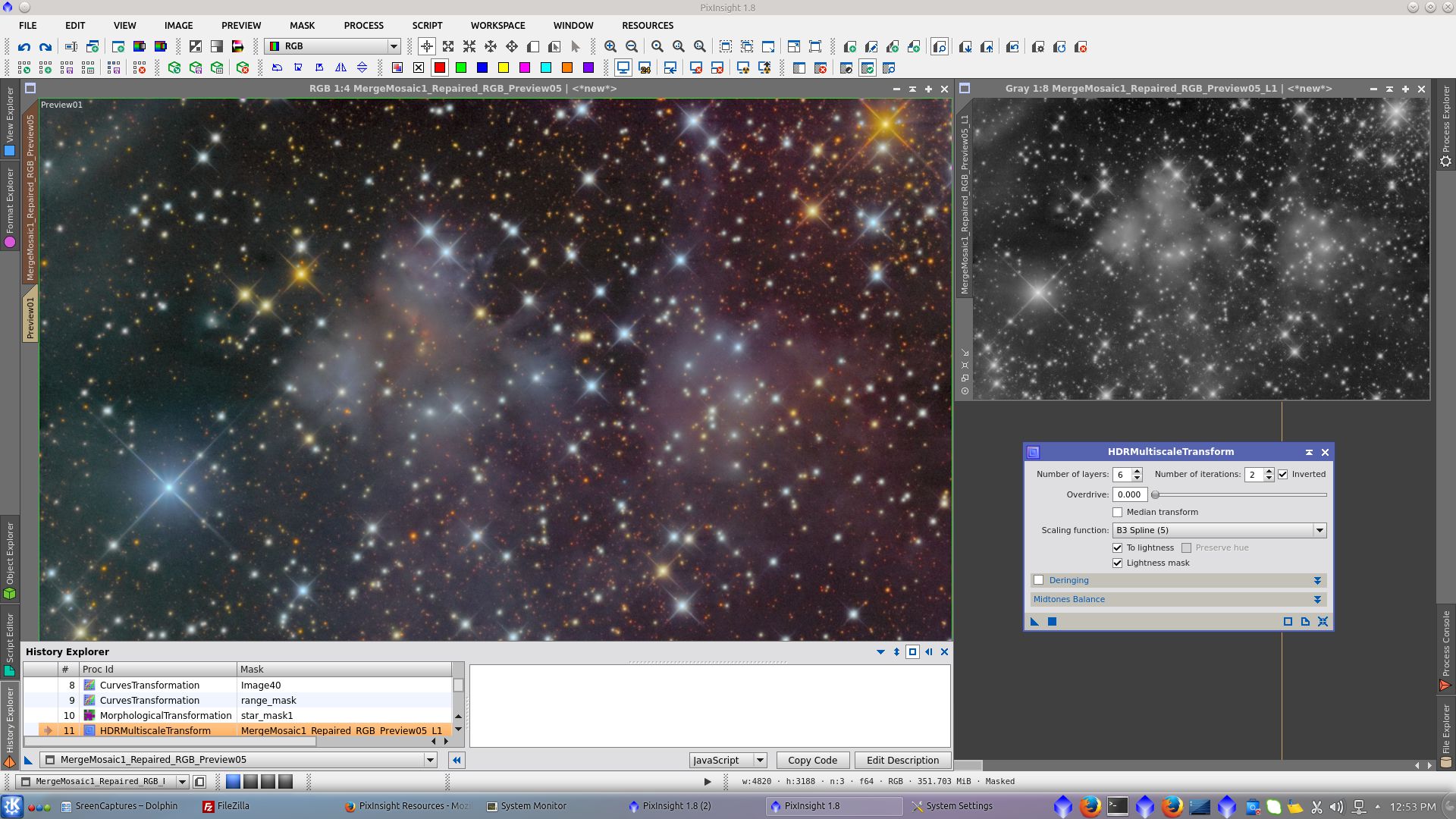
Over the L image apply RangeSelection tool to generate a rangemask to be used for protection of background and stars while using MultiscaleLinerTransform to give contrast in the small scale bright areas of the nebula, including little stars, increasing Bias in the smallest layers
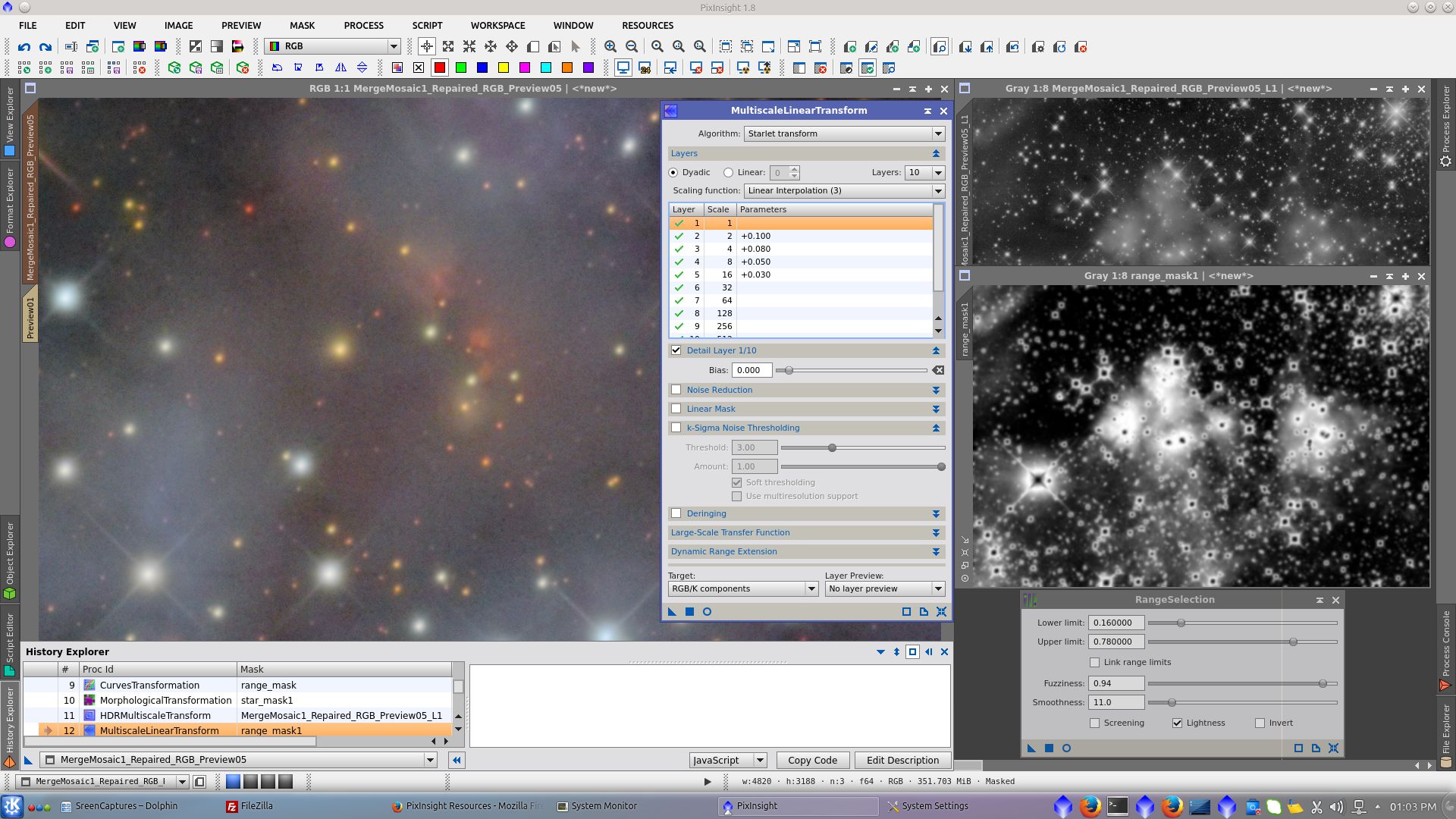
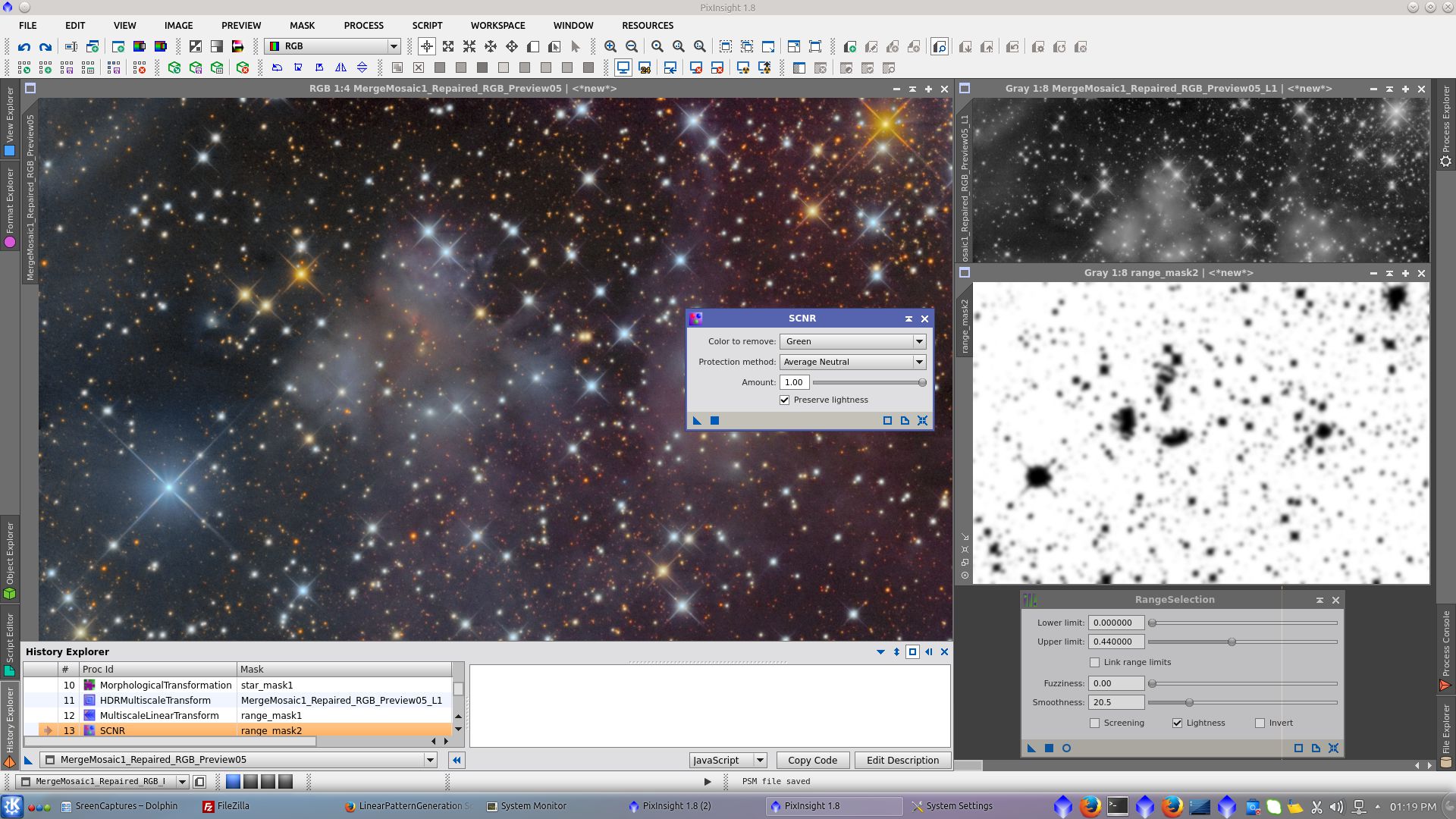
Over the L image apply RangeSelection tool to generate a rangemask to be used for protection of stars while using SCNR tool for decreasing the green cast
Assign Profile to the image
Increase Saturation protecting the background with L
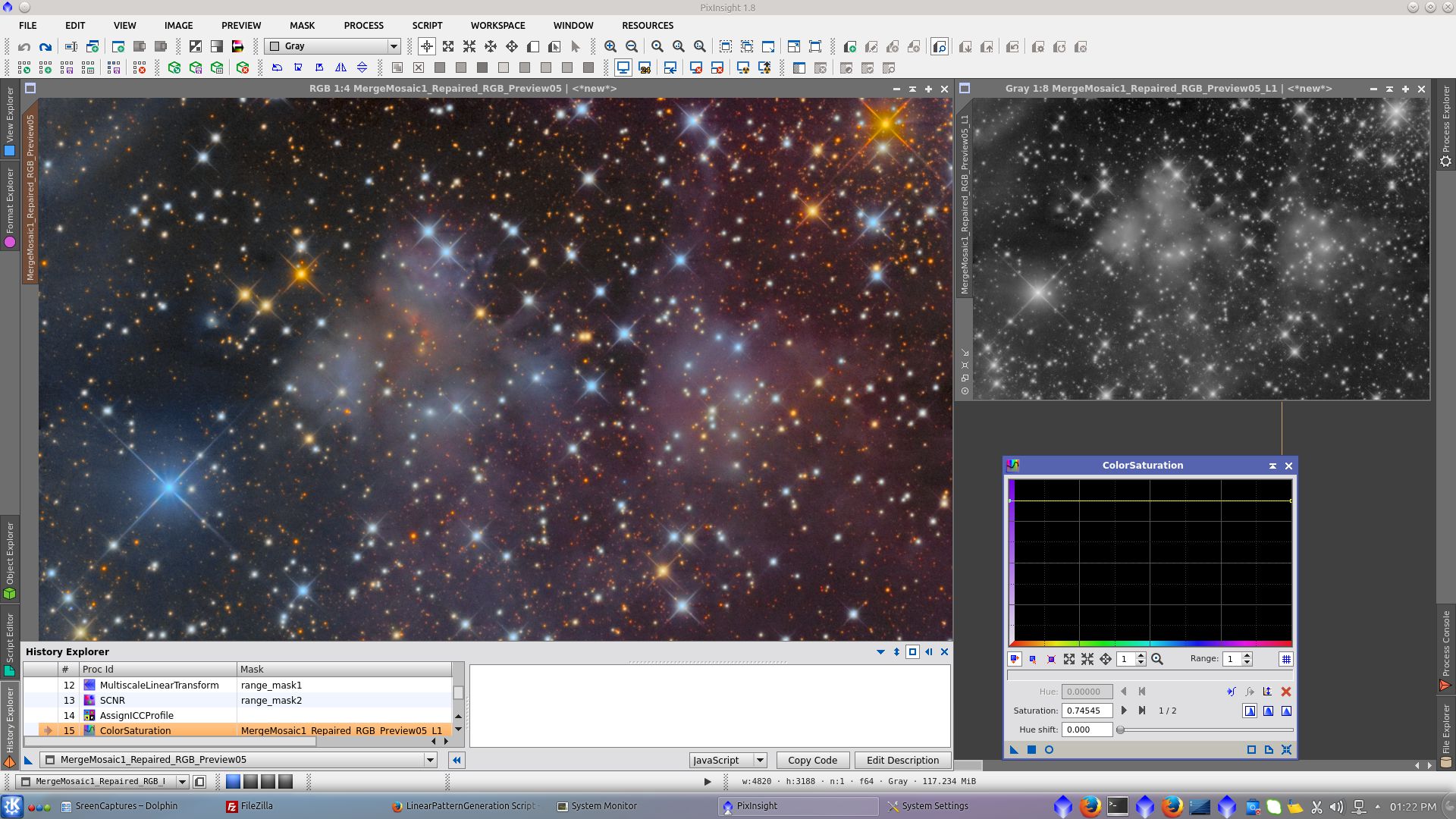
Over the previously created starmask apply two MorphologicalTransformation process to expand the area of protection
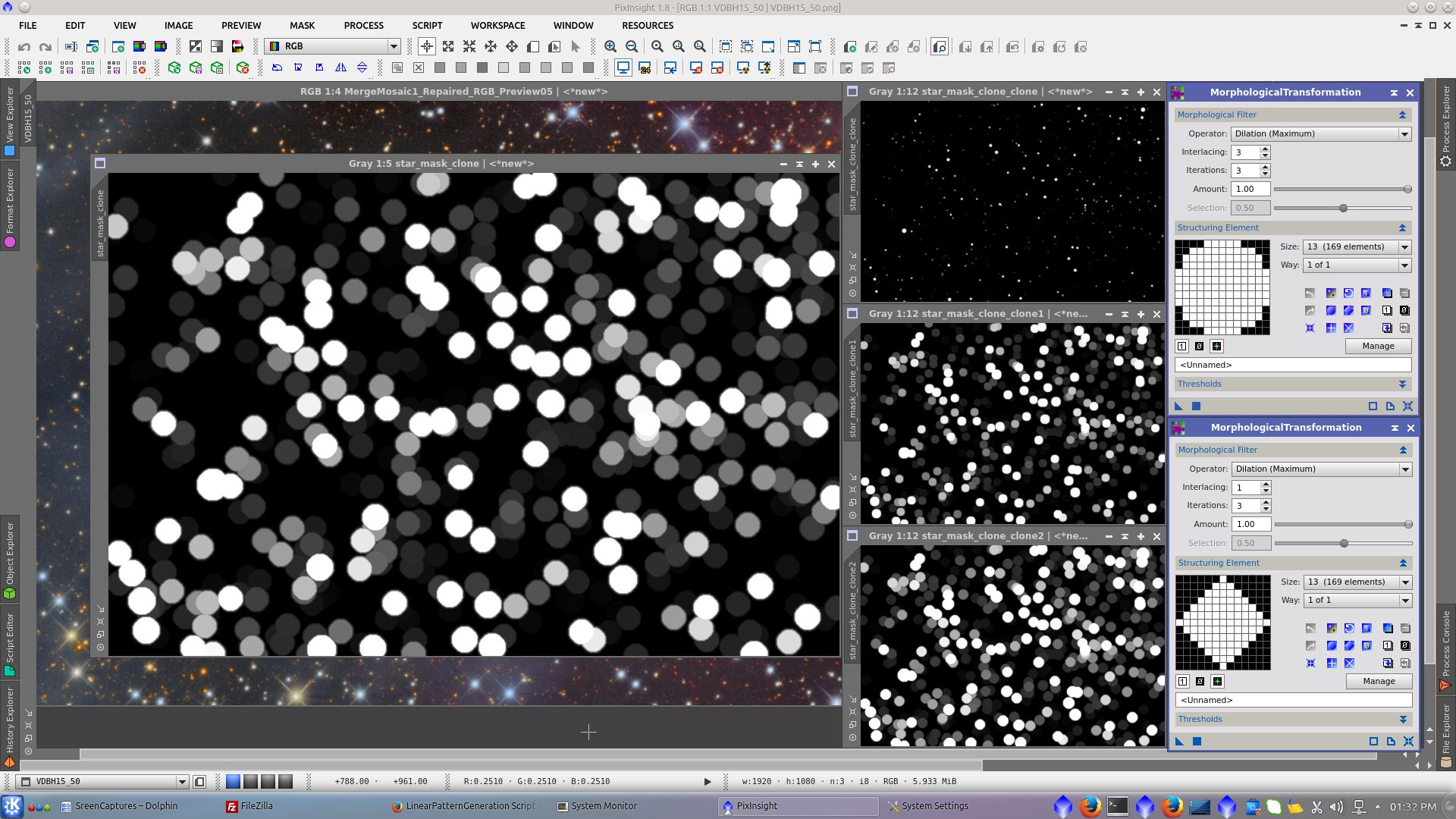
With the new mask protecting the background apply ACDNR to Chrominance to reduce the increased chrominance noise from color saturation
Decrease Blue using SCNR and protecting the nebula with the previously created range_mask
Rotate the image for publication
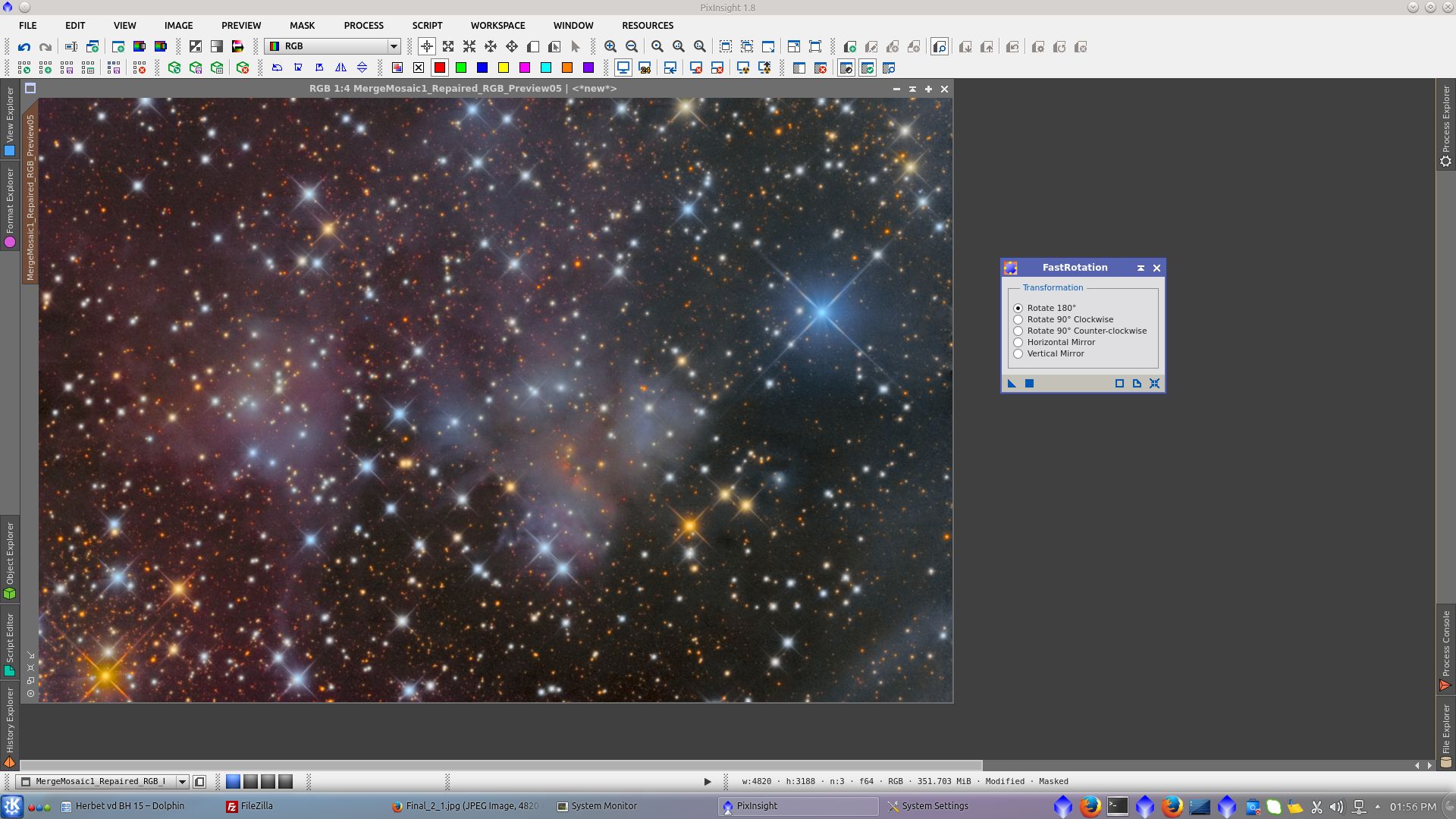
Final Image
